2025-05-12 北海道大学
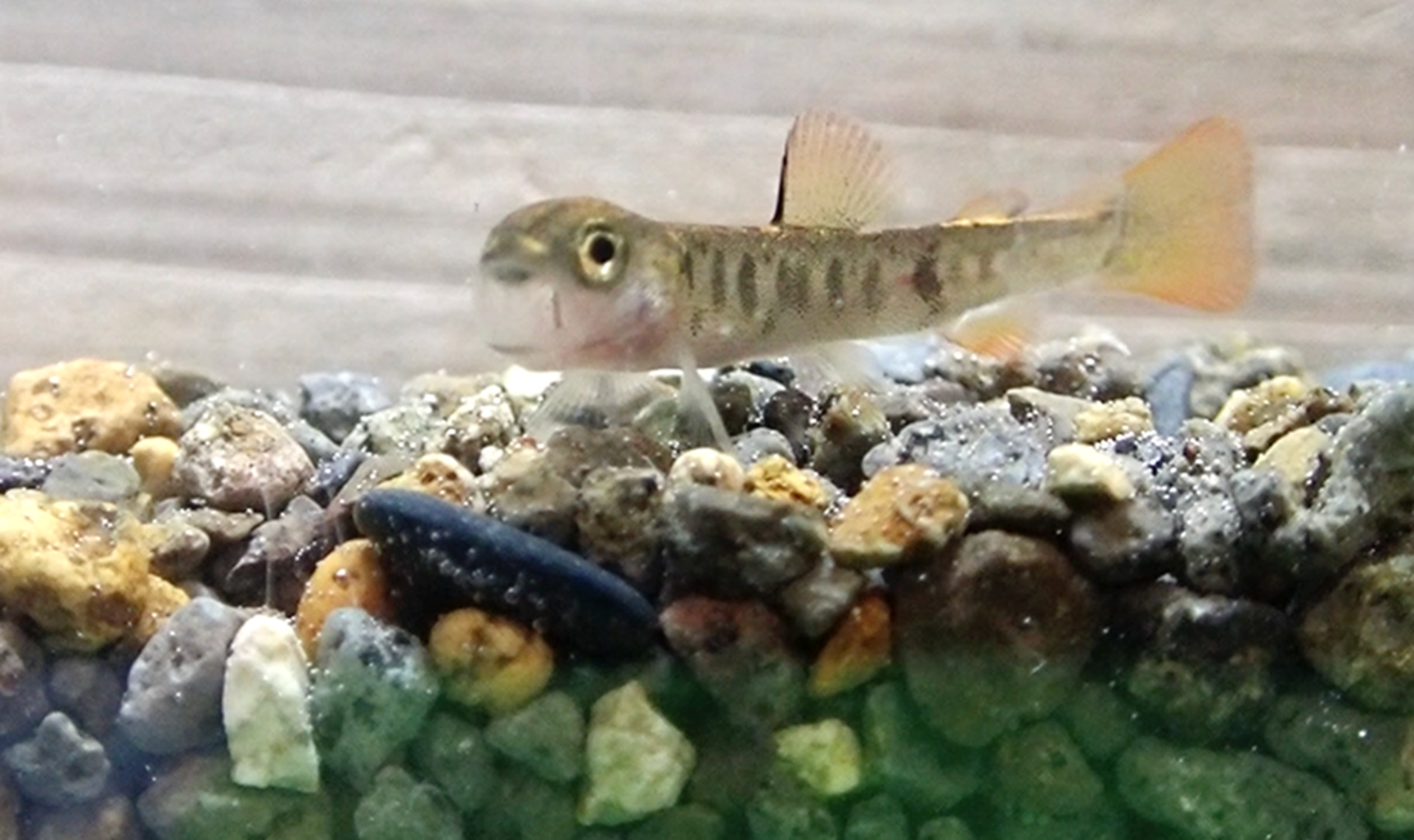

あくびをするイワナの稚魚
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/2025/05/post-1878.html
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/250512_pr3.pdf
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10164-025-00844-w
魚のあくび:イワナSalvelinus leucomaenisの稚魚におけるあくび行動の個体群間変異 Fish yawn: interpopulation variation in yawning characteristics of juvenile white-spotted char Salvelinus leucomaenis
Reo Nagasaka,Hiroyuki Yamada & Satoshi Wada
Journal of Ethology Published:05 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10164-025-00844-w
Abstract
Yawning is a stereotyped behavior and is prevalent across vertebrates, including fish. Although intraspecific variation of yawning behavior in a population has been observed in several taxa, no studies have demonstrated differences in yawning behavior among populations. This study compared yawning behavior among four local populations of juvenile white-spotted char Salvelinus leucomaenis. Although there were no differences in the frequency of yawning among the populations, the duration of yawns differed significantly among the local populations, within each of two behavioral states of juveniles, i.e., during swimming and during station-holding behavior, in which juveniles are sedentary on the substrate. The juveniles from Station 1 showed yawns with shorter duration than those from Stations 2 and 3 during station-holding behavior. Juveniles from Station 2 showed yawns with longer duration than those from Station 4 during swimming. Although we could not determine any ecological or evolutionary factors behind the variations in yawn duration, yawning behavior could be affected by local environmental factors, such as predation pressure. This is the first study demonstrating interpopulation variation of yawning behavior in animals.