2025-08-05 中国科学院(CAS)
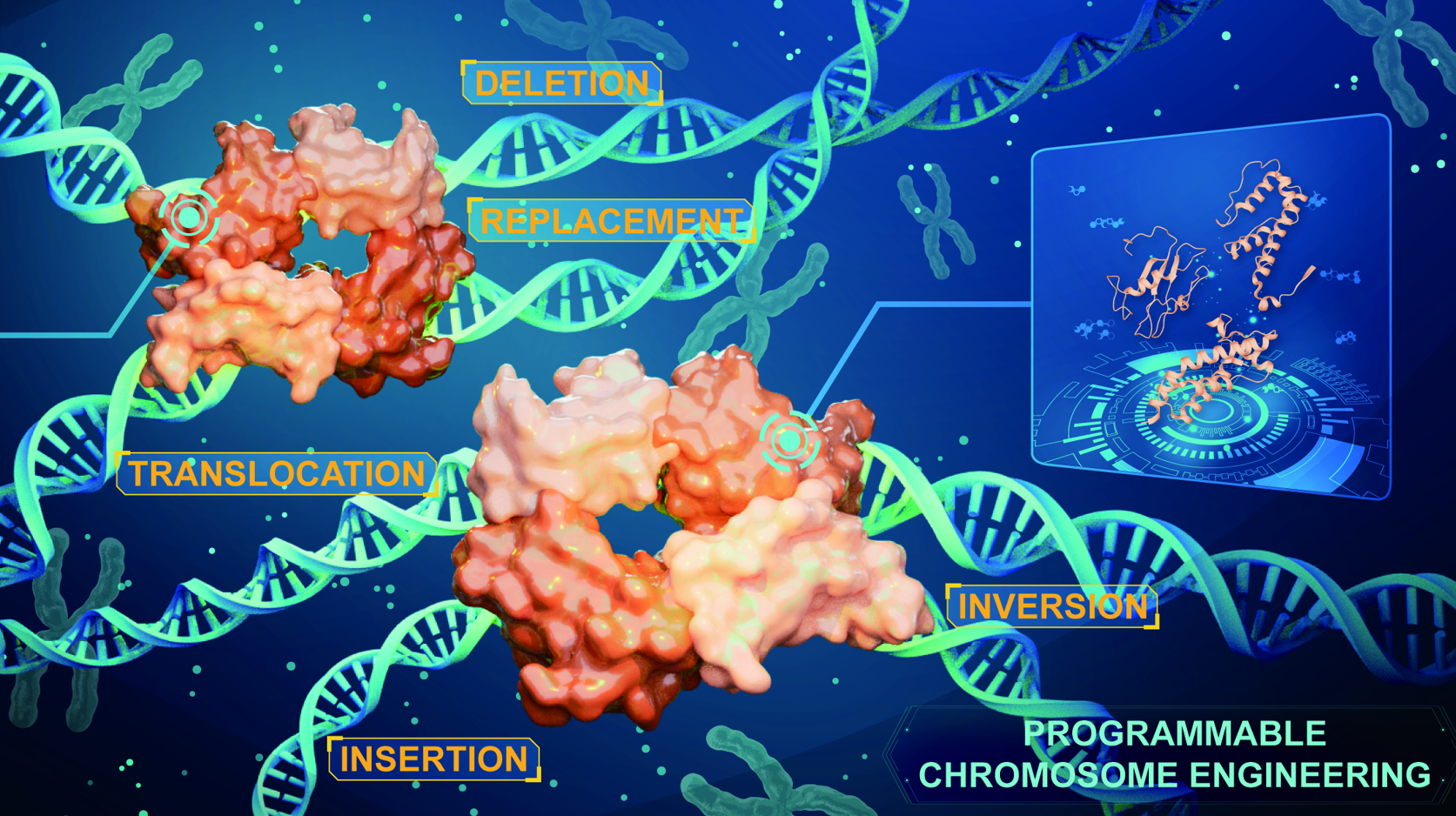
Iterative recombinase technologies mediate precision chromosome engineering (Image by IGDB)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202508/t20250804_1048985.shtml
- https://www.cell.com/cell/abstract/S0092-8674(25)00800-1
キロベースからメガベース規模のゲノム工学を効率的かつ正確に行うための反復型組み換え酵素技術 Iterative recombinase technologies for efficient and precise genome engineering across kilobase to megabase scales
Chao Sun ∙ Hongchao Li ∙ Yijing Liu ∙ … ∙ Jinxing Liu ∙ Ronghong Liang ∙ Caixia Gao
Cell Published:August 4, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2025.07.011
Highlights
- High-throughput profiling enables precise retrofitting of recombination sites
- AI-guided recombinase engineering enhances recombination efficiency
- A scar-free strategy enables seamless chromosome editing without residual sequences
- The PCE systems support programmable chromosome engineering in plants and human cells
Summary
Genome editing technologies face challenges in achieving precise, large-scale DNA manipulations in higher organisms, including inefficiency, limited editing scales and types, and the retention of undesired sequences such as recombination sites (“scars”). Here, we present programmable chromosome engineering (PCE) and RePCE, two programmable chromosome editing systems enabling scarless kilobase-to-megabase DNA manipulations in plants and human cells. Through high-throughput engineering, we obtained Lox sites with a 10-fold reduced reversibility and applied an AI-assisted recombinase engineering method (AiCErec) to generate Cre variants with 3.5 times the recombination efficiency of the wild type. Incorporation of a Re-pegRNA-mediated scar-free strategy further enhanced editing precision, allowing scarless insertions, deletions, replacements, inversions, and translocations at the chromosomal level. Key applications include a 315-kb inversion in rice conferring herbicide resistance, scarless chromosome fusions, and a 12-Mb inversion at human disease-related sites. These advances significantly broaden the scope of genome editing applications in molecular breeding, therapeutic development, and synthetic biology.