2025-08-20 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/new-graphene-technology-matures-brain-organoids-faster-may-unlock-neurodegenerative-insights
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-62637-6
疾患モデル、幹細胞の成熟、およびバイオハイブリッドロボティクスにおける非遺伝的ニューロモジュレーションのためのグラフェン光電子アクチュエーター Non-genetic neuromodulation with graphene optoelectronic actuators for disease models, stem cell maturation, and biohybrid robotics
Elena Molokanova,Teng Zhou,Pragna Vasupal,Volodymyr P. Cherkas,Prashant Narute,Mariana S. A. Ferraz,Michael Reiss,Angels Almenar-Queralt,Georgia Chaldaiopoulou,Janaina Sena de Souza,Honieh Hemati,Francisco Downey,Omowuyi O. Olajide,Carolina Thörn Perez,Francesca Puppo,Pinar Mesci,Samuel L. Pfaff,Dmitry Kireev,Alysson R. Muotri & Alex Savchenko
Nature Communications Published:20 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-62637-6
Abstract
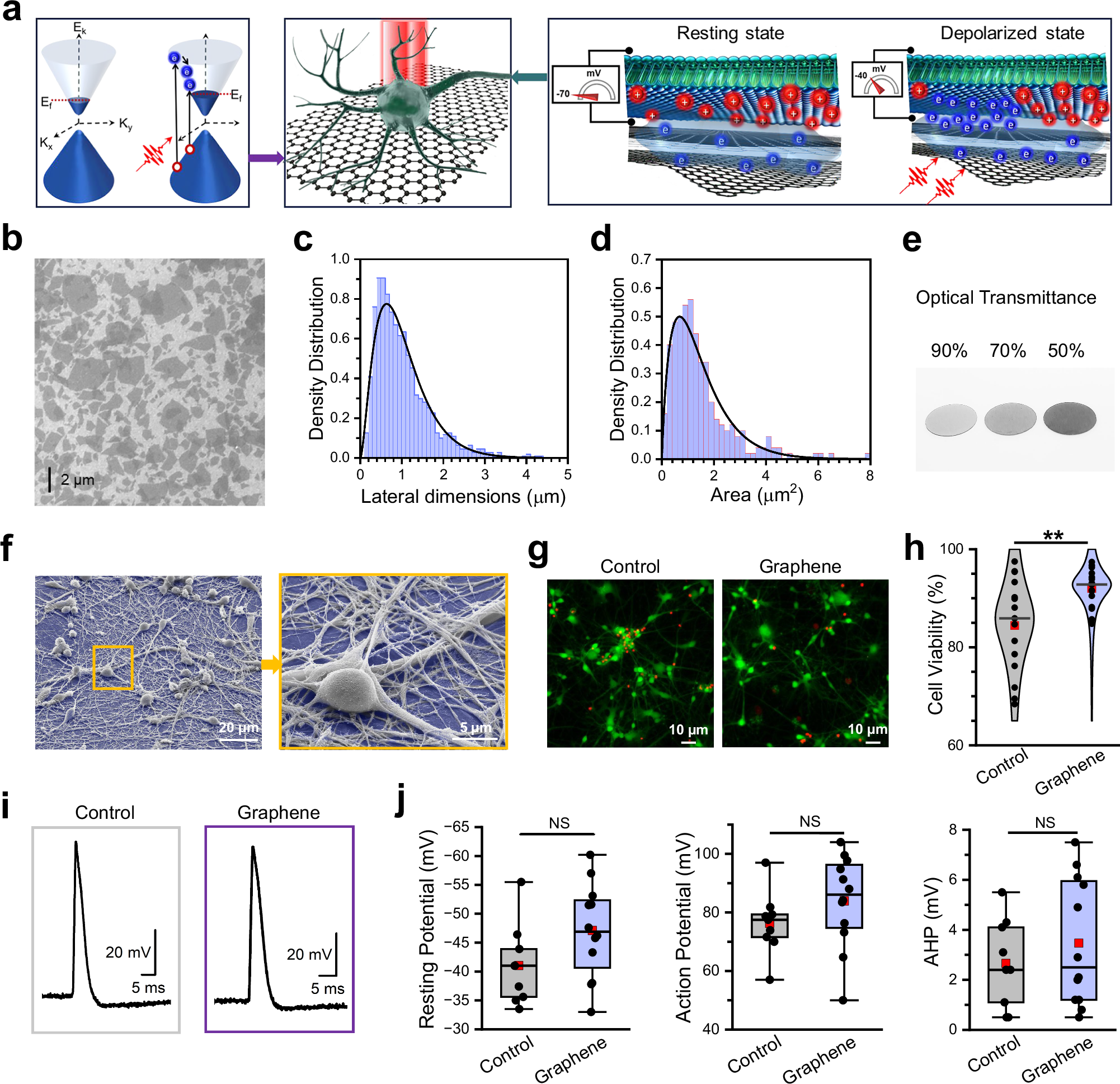
Light can serve as a tunable trigger for neurobioengineering technologies, enabling probing, control, and enhancement of brain function with unmatched spatiotemporal precision. Yet, these technologies often require genetic or structural alterations of neurons, disrupting their natural activity. Here, we introduce the Graphene-Mediated Optical Stimulation (GraMOS) platform, which leverages graphene’s optoelectronic properties and its ability to efficiently convert light into electricity. Using GraMOS in longitudinal studies, we found that repeated optical stimulation enhances the maturation of hiPSC-derived neurons and brain organoids, underscoring GraMOS’s potential for regenerative medicine and neurodevelopmental studies. To explore its potential for disease modeling, we applied short-term GraMOS to Alzheimer’s stem cell models, uncovering disease-associated alterations in neuronal activity. Finally, we demonstrated a proof-of-concept for neuroengineering applications by directing robotic movements with GraMOS-triggered signals from graphene-interfaced brain organoids. By enabling precise, non-invasive neural control across timescales from milliseconds to months, GraMOS opens new avenues in neurodevelopment, disease treatment, and robotics.