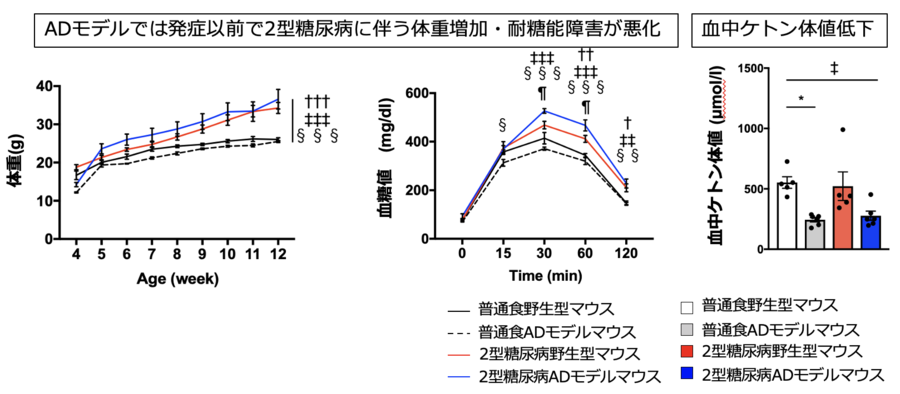
他の遺伝子とは異なり、生命の構成要素であるタンパク質をコードしない一種の遺伝子の正確な働きが、解明され始めている。 Scientists are starting to understand the precise workings of a type of gene that, unlike other genes, does not code for proteins – the building blocks of life.
2022-06-17 バース大学
ほとんどのlncRNA遺伝子の機能は謎のままだが、その一部は、遺伝子発現制御に関わるタンパク質をコードする隣接する遺伝子と一緒に脳内で共発現している。これらのlncRNA遺伝子と、タンパク質をコードする隣接する遺伝子は、一対となって働いているのである。特に、胚発生時や幼少期の脳において、神経細胞の発達と機能を制御しているのである。
今回の研究では、これらの遺伝子対のうちの1つのレベルを制御するのに関わる制御経路が説明されています。ゲノム上の位置と量は、その活性のタイミングと同様に、慎重に調整される必要があります。
lncRNAと、それが対になっている重要なタンパク質コード遺伝子の発現を調整するために働く重要なシグナル経路を特定しました。
<関連情報>
- https://www.bath.ac.uk/announcements/scientists-unravel-the-mystery-of-genes-that-are-key-to-brain-development/
- https://journals.plos.org/plosgenetics/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgen.1010230
神経細胞におけるPaupar-Pax6発現を調整するWnt応答性シス制御因子のクロマチン相互作用マップによる同定 Chromatin interaction maps identify Wnt responsive cis-regulatory elements coordinating Paupar-Pax6 expression in neuronal cells
Ioanna Pavlaki ,Michael Shapiro ,Giuseppina Pisignano,Stephanie M. E. Jones,Jelena Telenius,Silvia Muñoz-Descalzo,Robert J. Williams,Jim R. Hughes,Keith W. Vance
PLOS Genetics Published: June 16, 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1010230
Abstract
Central nervous system-expressed long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are often located in the genome close to protein coding genes involved in transcriptional control. Such lncRNA-protein coding gene pairs are frequently temporally and spatially co-expressed in the nervous system and are predicted to act together to regulate neuronal development and function. Although some of these lncRNAs also bind and modulate the activity of the encoded transcription factors, the regulatory mechanisms controlling co-expression of neighbouring lncRNA-protein coding genes remain unclear. Here, we used high resolution NG Capture-C to map the cis-regulatory interaction landscape of the key neuro-developmental Paupar-Pax6 lncRNA-mRNA locus. The results define chromatin architecture changes associated with high Paupar–Pax6 expression in neurons and identify both promoter selective as well as shared cis-regulatory-promoter interactions involved in regulating Paupar–Pax6 co-expression. We discovered that the TCF7L2 transcription factor, a regulator of chromatin architecture and major effector of the Wnt signalling pathway, binds to a subset of these candidate cis-regulatory elements to coordinate Paupar and Pax6 co-expression. We describe distinct roles for Paupar in Pax6 expression control and show that the Paupar DNA locus contains a TCF7L2 bound transcriptional silencer whilst the Paupar transcript can act as an activator of Pax6. Our work provides important insights into the chromatin interactions, signalling pathways and transcription factors controlling co-expression of adjacent lncRNAs and protein coding genes in the brain.