2023-07-03 コロンビア大学
◆RNAを標的とするCRISPRは、RNAの編集や遺伝子の発現抑制、有望な薬剤候補の同定など、さまざまな応用が期待されています。この研究によって、RNAを標的とするCRISPRツールのオンターゲットおよびオフターゲットの活性を予測する新たな手法が開発されたことが示されました。
<関連情報>
- https://www.engineering.columbia.edu/news/ai-and-crispr-precisely-control-gene-expression
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-023-01830-8
ディープラーニングを用いたCRISPR-Cas13dガイドRNAのオンターゲットおよびオフターゲット活性の予測 Prediction of on-target and off-target activity of CRISPR–Cas13d guide RNAs using deep learning
Hans-Hermann Wessels,Andrew Stirn,Alejandro Méndez-Mancilla,Eric J. Kim,Sydney K. Hart,David A. Knowles & Neville E. Sanjana
Nature Biotechnology Published:03 July 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-023-01830-8
Abstract
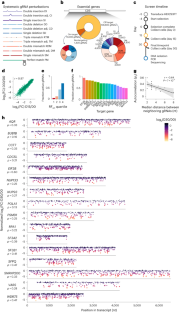
Transcriptome engineering applications in living cells with RNA-targeting CRISPR effectors depend on accurate prediction of on-target activity and off-target avoidance. Here we design and test ~200,000 RfxCas13d guide RNAs targeting essential genes in human cells with systematically designed mismatches and insertions and deletions (indels). We find that mismatches and indels have a position- and context-dependent impact on Cas13d activity, and mismatches that result in G–U wobble pairings are better tolerated than other single-base mismatches. Using this large-scale dataset, we train a convolutional neural network that we term targeted inhibition of gene expression via gRNA design (TIGER) to predict efficacy from guide sequence and context. TIGER outperforms the existing models at predicting on-target and off-target activity on our dataset and published datasets. We show that TIGER scoring combined with specific mismatches yields the first general framework to modulate transcript expression, enabling the use of RNA-targeting CRISPRs to precisely control gene dosage.