2025-09-17 バーミンガム大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.birmingham.ac.uk/news/2025/new-data-sheds-light-on-immunotherapy-failure-bringing-hope-to-patients-with-cancer
- https://www.thno.org/v15p7501.htm
分泌されたClever-1はT細胞応答を調節し、癌免疫療法の有効性に影響を与える Secreted Clever-1 modulates T cell responses and impacts cancer immunotherapy efficacy
Stuart Prince, Miro Viitala, Riikka Sjöroos, Ábris Á. Bendes,, Jenna H. Rannikko, Daniel A. Patten, Ilaria di Benedetto, Rita Turpin, Arno Ylitalo, Laura Tyni, Carlos R. Figueiredo, Pia Boström, Ilkka Koskivuo, Tiina A. Salminen, Shishir Shetty, Maija Hollmén
Theranostics Published: 2025-6-23
DOI:10.7150/thno.110544
Abstract
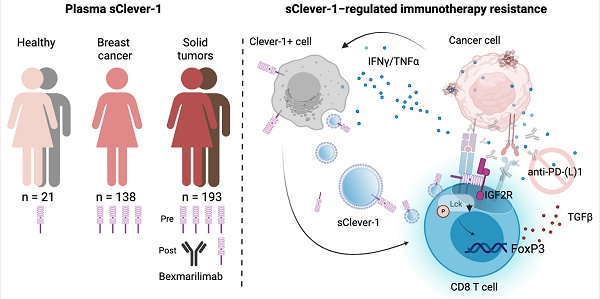
Rationale: Clever-1 is a multifunctional scavenger receptor that promotes immunosuppressive activity in macrophages, contributing to tumor immune evasion. Its high expression correlates with resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors, and co-targeting Clever-1 with anti-PD-1 enhances therapeutic efficacy in refractory tumor models. The humanized anti-Clever-1 IgG4 antibody, bexmarilimab, is under clinical investigation for treating solid tumors (NCT03733990) and hematological malignancies (NCT05428969).
Methods: To assess the impact of Clever-1 in cancer, we analyzed plasma samples from breast cancer patients (n=139) and bexmarilimab-treated clinical trial participants (n=193) using TRFIA-based ELISA to quantify secreted Clever-1 (sClever-1). A recombinant sClever-1 protein was produced and characterized biophysically. Functional assays, including flow cytometry, Western blotting, T cell activation, and Jurkat reporter systems, were used to assess interactions with T cells. Mechanistic studies involved extracellular vesicle isolation, pulldown assays, and mass spectrometry. Inhibitor studies and patient-derived tumor explants were used to evaluate the immunomodulatory impact of sClever-1 and its effect on anti-PD-1 responses.
Results: sClever-1 was significantly enriched in the plasma of cancer patients and reduced following bexmarilimab treatment. Its release was induced by IFNγ/LPS via serine protease-dependent cleavage. The recombinant sClever-1 bound selectively to activated T cells via mannose-6-phosphate-mediated interaction with IGF2R, impairing TCR signaling and Th1 expansion. sClever-1 was also associated with macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles and contributed to T cell tolerance and reduced anti-PD-1 efficacy. In tumor explants, sClever-1 bound to activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and increased TGFβ secretion.
Conclusions: These findings identify sClever-1 as a previously unrecognized, immunosuppressive mediator in cancer that operates independently of cellular Clever-1 expression. sClever-1 may serve as both a therapeutic target and biomarker to guide immunotherapy strategies.


