2025-10-07 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
Credit: Corrine Smolen/Girirajan Laboratory / Penn State. Creative Commons
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/eberly-college-science/story/background-genetic-variants-influence-clinical-features-complex
- https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(25)01080-3
遺伝子修飾因子と確認は複雑な疾患の多様な表現度を駆動する Genetic modifiers and ascertainment drive variable expressivity of complex disorders
Matthew Jensen ∙ Corrine Smolen ∙ Anastasia Tyryshkina ∙ … ∙ Corrado Romano ∙ Joris Andrieux ∙ Santhosh Girirajan
Cell Published:October 7, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2025.09.012
Highlights
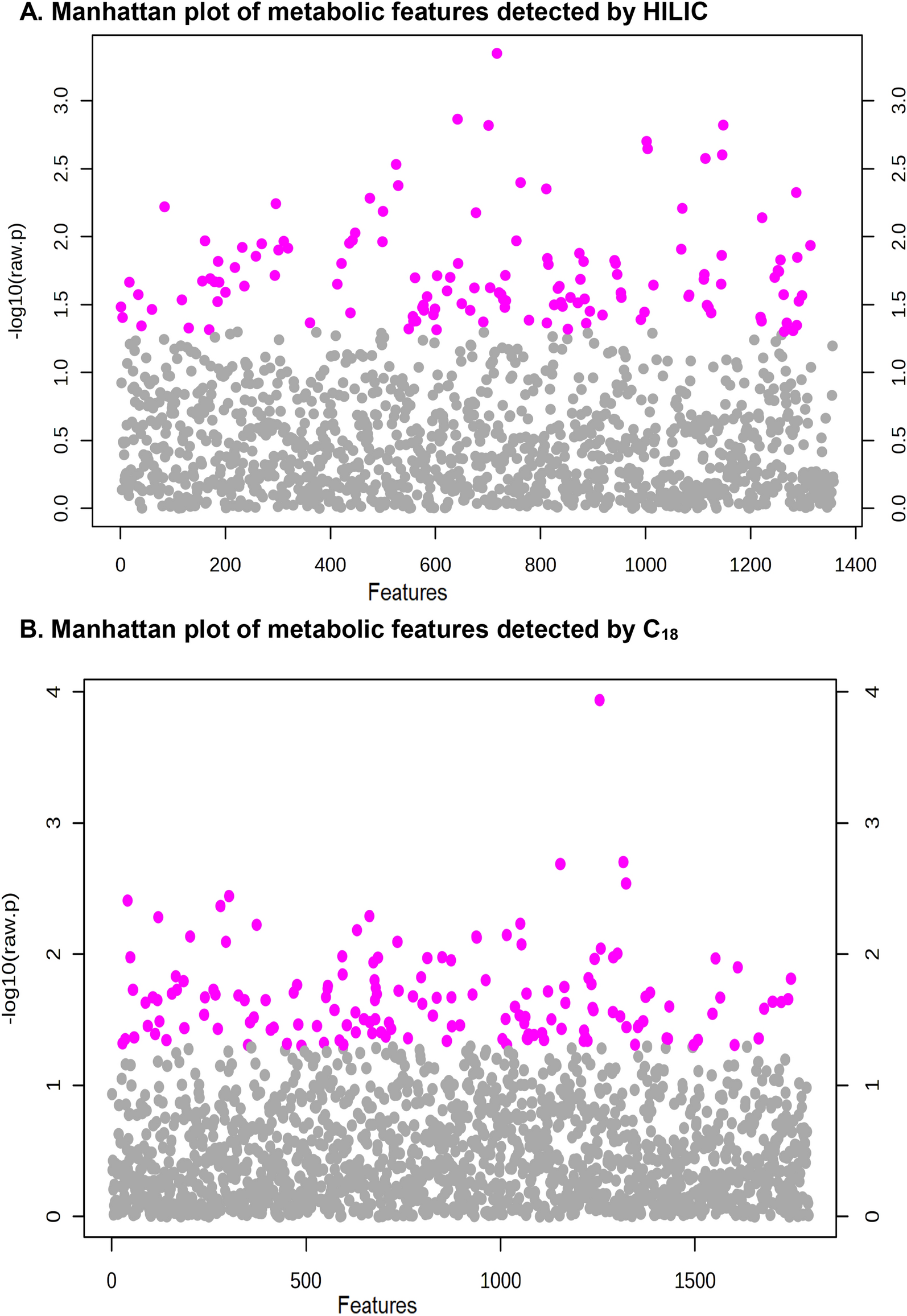
- Disease-associated variants show extensive phenotypic variability
- The genetic background modifies the expressivity of neurodevelopmental phenotypes
- Modifier effects are disease, population, and primary-variant specific
- Ascertainment bias confounds genotype-phenotype studies
Summary
Variable expressivity of disease-associated variants implies a role for secondary variants that modify clinical features. We assessed the effects of modifier variants on the clinical outcomes of 2,455 individuals with primary variants. Among 124 families with the 16p12.1 deletion, distinct rare and common variant classes conferred risks for specific developmental features, including short tandem repeats for neurological defects. Network analysis suggested distinct mechanisms involving 16p12.1 genes and secondary variants specific to each proband. Within disease and population cohorts of 976 individuals with the 16p12.1 deletion, we found opposing effects of secondary variants on clinical features across ascertainments. Additional analysis of 1,479 probands with other primary variants, such as the 16p11.2 deletion and CHD8 variants, and 1,528 probands without primary variants showed that phenotypic associations differed by primary variant context and were influenced by synergistic interactions between primary and secondary variants. Our study provides a paradigm to dissect the personalized genomic architecture of complex disorders.