2025-11-11 スウェーデン王立工科大学(KTH)
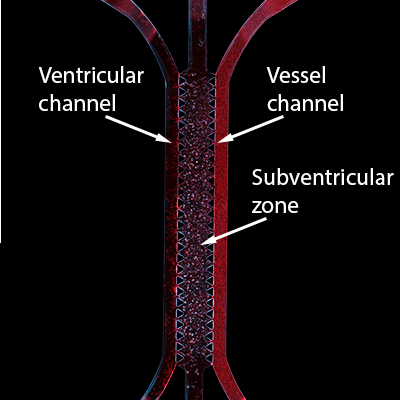
A partial view of the prenatal brain model: a microchip consisting of three channels with human cells: the ventricular channel, the sub ventricular zone with neural stem cells and glia, and the blood vessel channel. Each channel is about 1 cm long.
<関連情報>
- https://www.kth.se/en/om/nyheter/centrala-nyheter/potential-treatment-may-prevent-brain-damage-in-premature-babies-1.1438415
- https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.202502145
脳室下帯オンチップ:新生児脳室内出血における神経新生阻害を研究するためのモデル Subventricular Zone-on-a-Chip: A Model to Study Neurogenesis Disruption in Neonatal Intraventricular Hemorrhage
Laura Nicoleti Zamproni, Begüm Gökçe, Magnus Gram, Coco Holliday, Aylin Sendemir, Marimélia Aparecida Porcionatto, Anna Herland
Advanced Science Published: 24 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202502145
Abstract
Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) in preterm infants disrupts neurogenesis in the subventricular zone (SVZ), a key neurogenic niche, yet no effective treatments exist. This work develops a human SVZ-on-a-chip model to investigate the inflammatory response in IVH and its impact on neurogenesis. Using this platform, this work examines the effects of red blood cell lysate (RBCL) and hemorrhagic cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from preterm infants with IVH on SVZ cells. Transcriptomic analysis reveal activation of inflammatory pathways in fetal astrocytes and brain microvascular endothelial cells exposed to hemoglobin isoforms. Notably, interleukin-1B (IL1B) is upregulated following RBCL and hemorrhagic CSF exposure. To probe its role, this work applies an IL1 receptor antagonist, which demonstrate that IL1B has a partially protective influence on neurogenesis. These findings highlight the SVZ-on-a-chip as a powerful tool for studying IVH pathology and emphasize the role of inflammation in regulating neurogenesis. IL1B emerges as a potential therapeutic target, offering new avenues for intervention. This study advances the understanding of IVH and lays the groundwork for developing strategies to protect the developing brain.


