2025-11-20 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202511/t20251121_1132540.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-025-01561-y
組織pHと前立腺特異抗原活性を介して前立腺腫瘍の悪性度をin situで分類するためのラベルフリーナビゲーションシステム Label-free navigation system for grading prostate tumour malignancy in situ via tissue pH and prostate-specific antigen activity
Ziyi Jin,Sihui Chen,Xiaoyan Dong,Zheng Zhao,Huaiyang Zeng,Pengcheng Zhang,Hang Yin,Suhongrui Zhou,Changle Li,Chang He,Jiaqi Huang,Jun Zhang,Jie Cheng,Hairong Zheng,Jinhua Yu,Hui Yang,Hang Wang & Cong Li
Nature Biomedical Engineering Published:18 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-025-01561-y
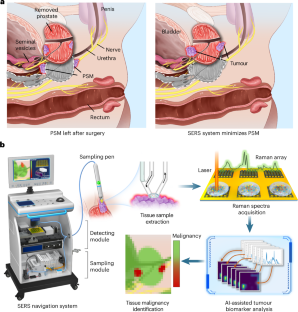
Abstract
Radical prostatectomy is a standard curative approach for high-risk prostate cancer, yet accurately defining tumour margins during surgery remains a major challenge. Intraoperative assessment of prostate tumour malignancy—particularly those with high aggressiveness catalogued in Gleason grade group (GG) ≥ 3—is crucial to prevent positive surgical margins and minimize postoperative complications. Here we develop a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-based navigation system for intraoperative localization of high-grade malignant regions by simultaneously accessing tissue acidity and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) enzymatic activity. This system integrates a sampling pen for automated biomarker extraction from tissue surfaces, a nano-imprinted SERS array producing a ratiometric Raman signal in response to acidity and PSA activity, and a two-dimensional deep-learning model for rapid Raman spectral interpretation. We show that the system can intraoperatively identify GG ≥ 3 malignancies in fresh prostate tissues from 144 Chinese patients with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.89. This SERS-based navigation system holds strong potential to enhance surgical precision, minimize tumour residue and ultimately improve patient outcomes.

