2022-04-21 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
各個人は、細胞の核の中にDNAという遺伝物質を持っています。DNAの塩基配列の1つの塩基に変異があると、人により遺伝子の違いが生じます。これはヌクレオチド多型と呼ばれ、CLLのような病気にかかりやすいなどの違いをもたらすことがあります。EPFLのシステム生物学・遺伝学研究室(生命科学部、Bart Deplancke教授)では、可変クロマチンモジュール(VCM)の形成機構を解明しようとしている。VCMは、ゲノムの分化単位で、遺伝子の発現や発現調節につながる協調的分子挙動を表すものである。
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/targeting-anti-tumor-genes-to-provide-better-treat/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-29625-6#Ack1
白血病予防のための生殖細胞変異体は、転写因子核形成を介してクロマチンモジュール形成を仲介する A leukemia-protective germline variant mediates chromatin module formation via transcription factor nucleation
Gerard Llimos,Vincent Gardeux,Ute Koch,Judith F. Kribelbauer,Antonina Hafner,Daniel Alpern,Joern Pezoldt,Maria Litovchenko,Julie Russeil,Riccardo Dainese,Riccardo Moia,Abdurraouf Mokhtar Mahmoud,Davide Rossi,Gianluca Gaidano,Christoph Plass,Pavlo Lutsik,Clarissa Gerhauser,Sebastian M. Waszak,Alistair Boettiger,Freddy Radtke &Bart Deplancke
Nature Published: 19 April 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29625-6
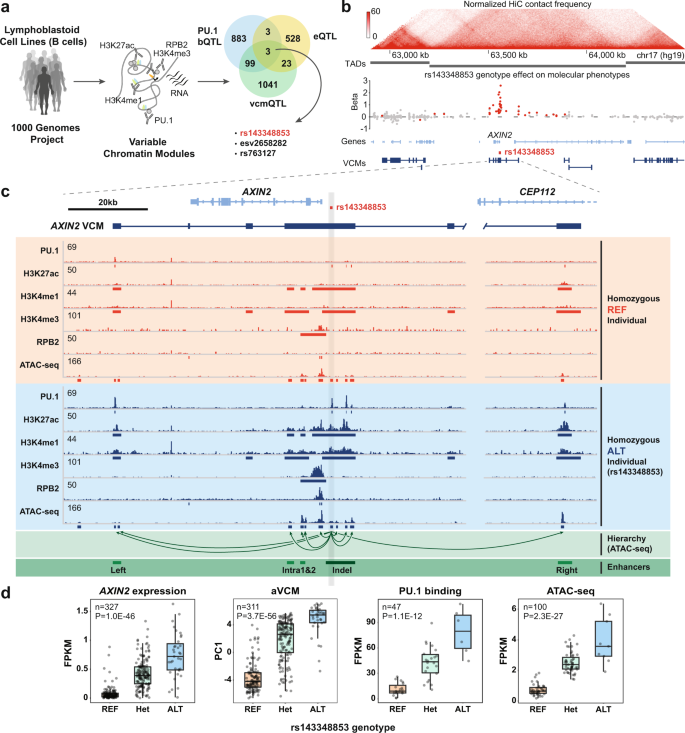
Fig. 1: rs143348853 indel activates the AXIN2 VCM in LCLs.
Abstract
Non-coding variants coordinate transcription factor (TF) binding and chromatin mark enrichment changes over regions spanning >100 kb. These molecularly coordinated regions are named “variable chromatin modules” (VCMs), providing a conceptual framework of how regulatory variation might shape complex traits. To better understand the molecular mechanisms underlying VCM formation, here, we mechanistically dissect a VCM-modulating noncoding variant that is associated with reduced chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) predisposition and disease progression. This common, germline variant constitutes a 5-bp indel that controls the activity of an AXIN2 gene-linked VCM by creating a MEF2 binding site, which, upon binding, activates a super-enhancer-like regulatory element. This triggers a large change in TF binding activity and chromatin state at an enhancer cluster spanning >150 kb, coinciding with subtle, long-range chromatin compaction and robust AXIN2 up-regulation. Our results support a model in which the indel acts as an AXIN2 VCM-activating TF nucleation event, which modulates CLL pathology.