2023-05-15 アリゾナ大学
◆アルツハイマー病は、認知症、記憶障害、人格の変化などの不可逆的な症状を引き起こす神経変性疾患であり、医学の最も困難な問題の一つです。この病気の原因が不明であるため、症状の治療は可能ですが、治療法を見つけることは難しいとされています。
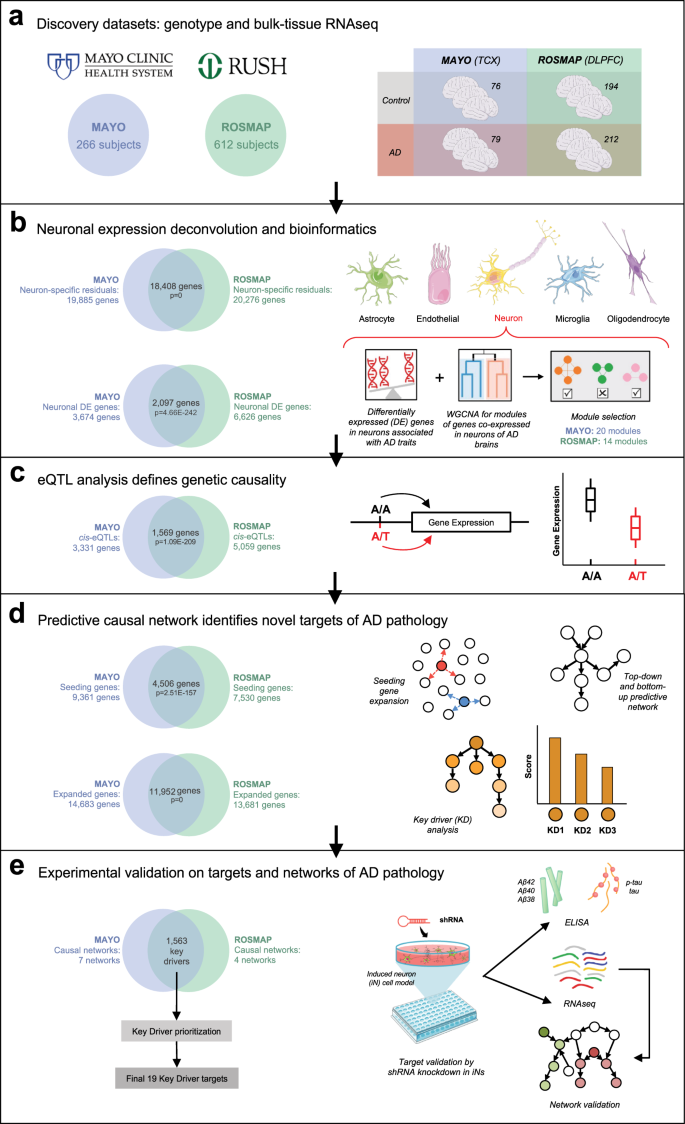
◆脳の組織サンプルを国立データベースから取得した2,000以上のアルツハイマー病の脳を対象に、チャン教授のAIアルゴリズムは遺伝子および分子プロセスに関する豊富な情報を活用し、人間の脳の計算ネットワークモデルを作り出しました。チームは今や、協調して働く全ゲノム遺伝子のマップを見ることができ、アルツハイマー病の発症の手がかりを提供し、健康から病気への分子的な経路を追跡することができます。
<関連情報>
- https://news.arizona.edu/story/scientists-use-ai-identify-likely-drug-targets-search-alzheimers-cure
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-023-04791-5
予測ネットワーク解析により、JMJD6をはじめとするアルツハイマー病のキードライバー候補を特定 Predictive network analysis identifies JMJD6 and other potential key drivers in Alzheimer’s disease
Julie P. Merchant,Kuixi Zhu,Marc Y. R. Henrion,Syed S. A. Zaidi,Branden Lau,Sara Moein,Melissa L. Alamprese,Richard V. Pearse II,David A. Bennett,Nilüfer Ertekin-Taner,Tracy L. Young-Pearse & Rui Chang
Communications Biology Published:15 May 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-023-04791-5
Abstract
Despite decades of genetic studies on late-onset Alzheimer’s disease, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. To better comprehend its complex etiology, we use an integrative approach to build robust predictive (causal) network models using two large human multi-omics datasets. We delineate bulk-tissue gene expression into single cell-type gene expression and integrate clinical and pathologic traits, single nucleotide variation, and deconvoluted gene expression for the construction of cell type-specific predictive network models. Here, we focus on neuron-specific network models and prioritize 19 predicted key drivers modulating Alzheimer’s pathology, which we then validate by knockdown in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons. We find that neuronal knockdown of 10 of the 19 targets significantly modulates levels of amyloid-beta and/or phosphorylated tau peptides, most notably JMJD6. We also confirm our network structure by RNA sequencing in the neurons following knockdown of each of the 10 targets, which additionally predicts that they are upstream regulators of REST and VGF. Our work thus identifies robust neuronal key drivers of the Alzheimer’s-associated network state which may represent therapeutic targets with relevance to both amyloid and tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease.