2023-11-09 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)

The ŌURA ring is a smart wearable produced by Finland-based company Oura Ring, which the researchers used to track skin temperature
◆長年、女性の生理周期による変動は医学研究への参加を妨げてきたが、この研究では、女性と男性の皮膚温度の比較から、生理周期や性別によるデータの違いが統計的に重要でないことが示された。この結果は、女性の生理的な周期がデータの解析に大きな障害となることを示唆しているわけではない。
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/women-produce-skin-temperature-data-that-is-just-as-predictable-as-men
- https://bsd.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13293-023-00558-z
ウェアラブルデバイスで記録された体温測定の生物学的性別によるばらつき Variability of temperature measurements recorded by a wearable device by biological sex
Lauryn Keeler Bruce,Patrick Kasl,Severine Soltani,Varun K. Viswanath,Wendy Hartogensis,Stephan Dilchert,Frederick M. Hecht,Anoushka Chowdhary,Claudine Anglo,Leena Pandya,Subhasis Dasgupta,Ilkay Altintas,Amarnath Gupta,Ashley E. Mason & Benjamin L. Smarr
Biology of Sex Differences Published:01 November 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s13293-023-00558-z
Abstract
Background
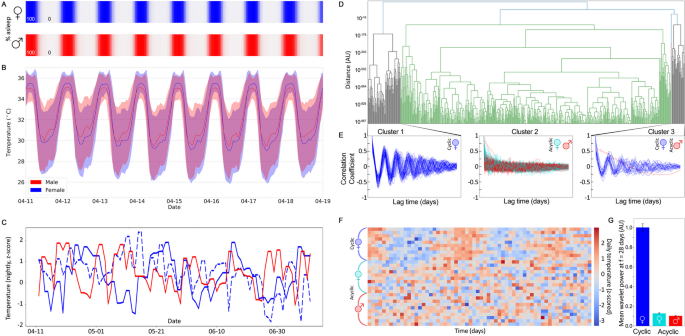
Females have been historically excluded from biomedical research due in part to the documented presumption that results with male subjects will generalize effectively to females. This has been justified in part by the assumption that ovarian rhythms will increase the overall variance of pooled random samples. But not all variance in samples is random. Human biometrics are continuously changing in response to stimuli and biological rhythms; single measurements taken sporadically do not easily support exploration of variance across time scales. Recently we reported that in mice, core body temperature measured longitudinally shows higher variance in males than cycling females, both within and across individuals at multiple time scales.
Methods
Here, we explore longitudinal human distal body temperature, measured by a wearable sensor device (Oura Ring), for 6 months in females and males ranging in age from 20 to 79 years. In this study, we did not limit the comparisons to female versus male, but instead we developed a method for categorizing individuals as cyclic or acyclic depending on the presence of a roughly monthly pattern to their nightly temperature. We then compared structure and variance across time scales using multiple standard instruments.
Results
Sex differences exist as expected, but across multiple statistical comparisons and timescales, there was no one group that consistently exceeded the others in variance. When variability was assessed across time, females, whether or not their temperature contained monthly cycles, did not significantly differ from males both on daily and monthly time scales.
Conclusions
These findings contradict the viewpoint that human females are too variable across menstrual cycles to include in biomedical research. Longitudinal temperature of females does not accumulate greater measurement error over time than do males and the majority of unexplained variance is within sex category, not between them.
Plain English Summary
Women are still excluded from research disproportionately, due in part to documented concerns that menstrual cycles make them more variable and so harder to study. In the past, we have challenged this claim, finding it does not hold for animal physiology, animal behavior, or human behavior. Here we are able to show that it does not hold in human physiology either. We analyzed 6 months of continuously collected temperature data measured by a commercial wearable device, in order to determine if it is true that females are more variable or less predictable than males. We found that temperatures mostly vary as a function of time of day and whether the individual was awake or asleep. Additionally, for some females, nightly maximum temperature contained a cyclical pattern with a period of around 28 days, consistent with menstrual cycles. The variability was different between cycling females, not cycling females, and males, but only cycling female temperature contained a monthly structure, making their changes more predictable than those of non-cycling females and males. We found the majority of unexplained variance to be within each sex/cycling category, not between them. All groups had indistinguishable measurement errors across time. This analysis of temperature suggests data-driven characteristics might be more helpful distinguishing individuals than historical categories such as binary sex. The work also supports the inclusion of females as subjects within biological research, as this inclusion does not weaken statistical comparisons, but does allow more equitable coverage of research results in the world.
Highlights
- Sex does not separate more and less variable individuals, as measured in continuous body temperature.
- Analysis of high-resolution, longitudinal temperature detailed here supports the inclusion of females in biomedical research.
- Cycling female variance in temperature is more structured across days and months than males, but most variance is within groups, and not between them.
- This work includes methods for identifying cycles in participant data without pre-existing labels.



