2024-04-12 スウォンジー大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.swansea.ac.uk/press-office/news-events/news/2024/04/choosing-sugary-drinks-over-fruit-juice-for-toddlers-linked-to-risk-of-adult-obesity.php
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41430-024-01430-y
砂糖入り飲料やフルーツジュースへの幼少期の暴露は、成人の脂肪率に異なる影響を与える Early exposure to sugar sweetened beverages or fruit juice differentially influences adult adiposity
David Benton & Hayley A. Young
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition Published:15 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-024-01430-y
Abstract
Objective
To examine associations between different types of sweet drinks consumed in early life and adult adiposity.
Design
The analysis involved the secondary analysis of the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children which followed children from birth to 24 years. Adiposity was measured using Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry while food frequency questionnaires and diaries monitored diet. ‘Early exposure’ to sweet drinks was defined as giving a sugar-sweetened beverage or 100% fruit juice (FJ), before two years of age.
Results
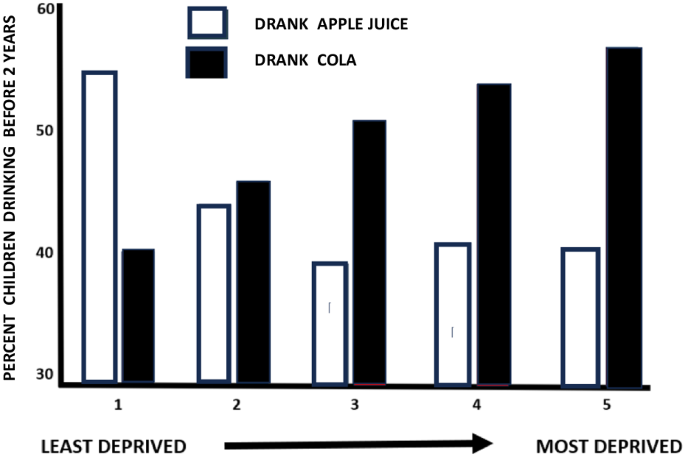
Early exposure to cola was associated with higher fat mass, android fat mass and BMI at age 24 years; whereas early exposure to apple juice was associated with lower adult adiposity in females but not males. When age three, exposure to cola was associated with a greater intake of energy, carbohydrates, protein, fat, and less fruit and more fried foods. In contrast, early exposure to apple juice was associated with higher protein and lower fat intakes and consuming more fruits/vegetables and less fried foods. Parental education, adiposity and socio-economic status influenced whether SSB or FJ was given to a child.
Conclusions
Early drinking of sugar sweetened beverages was associated with a less healthy dietary pattern, and greater adult adiposity. Early drinking of apple juice was associated with a healthier dietary pattern, and lower fat mass in adult females. The choice of drink was associated with social deprivation. As the dietary causes of adult obesity begin in early childhood, increased attention should be given to diet in the first years of life.