2024-06-07 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/scar-formation-after-spinal-cord-injury-is-more-complex-than-previously-thought
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-024-01678-4
マウスの外傷後の線維化における間質線維芽細胞の起源と部位依存的寄与の違い Distinct origin and region-dependent contribution of stromal fibroblasts to fibrosis following traumatic injury in mice
Daniel Holl,Wing Fung Hau,Anais Julien,Shervin Banitalebi,Jannis Kalkitsas,Soniya Savant,Enric Llorens-Bobadilla,Yann Herault,Guillaume Pavlovic,Mahmood Amiry-Moghaddam,David Oliveira Dias & Christian Göritz
Natural Neuroscience Published:07 June 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-024-01678-4
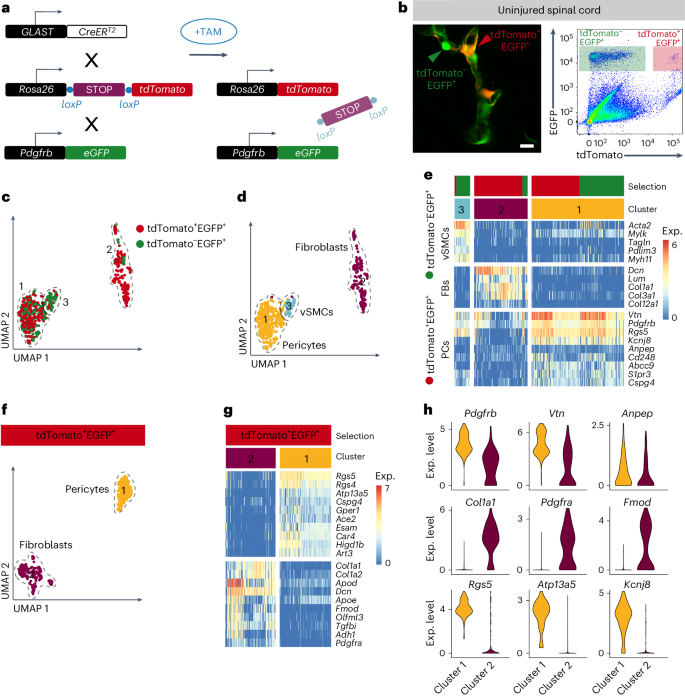
Abstract
Fibrotic scar tissue formation occurs in humans and mice. The fibrotic scar impairs tissue regeneration and functional recovery. However, the origin of scar-forming fibroblasts is unclear. Here, we show that stromal fibroblasts forming the fibrotic scar derive from two populations of perivascular cells after spinal cord injury (SCI) in adult mice of both sexes. We anatomically and transcriptionally identify the two cell populations as pericytes and perivascular fibroblasts. Fibroblasts and pericytes are enriched in the white and gray matter regions of the spinal cord, respectively. Both cell populations are recruited in response to SCI and inflammation. However, their contribution to fibrotic scar tissue depends on the location of the lesion. Upon injury, pericytes and perivascular fibroblasts become activated and transcriptionally converge on the generation of stromal myofibroblasts. Our results show that pericytes and perivascular fibroblasts contribute to the fibrotic scar in a region-dependent manner.