2024-07-16 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/correcting-mutations-that-cause-stroke.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-49982-8
HTRA1における病原性コンフォメーション異常の合理的修正 Rational correction of pathogenic conformational defects in HTRA1
Nathalie Beaufort,Linda Ingendahl,Melisa Merdanovic,Andree Schmidt,David Podlesainski,Tim Richter,Thorben Neumann,Michael Kuszner,Ingrid R. Vetter,Patricia Stege,Steven G. Burston,Anto Filipovic,Yasser B. Ruiz-Blanco,Kenny Bravo-Rodriguez,Joel Mieres-Perez,Christine Beuck,Stephan Uebel,Monika Zobawa,Jasmin Schillinger,Rainer Malik,Katalin Todorov-Völgyi,Juliana Rey,Annabell Roberti,Birte Hagemeier,… Martin Dichgans
Nature Communications Published:16 July 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-49982-8
Abstract
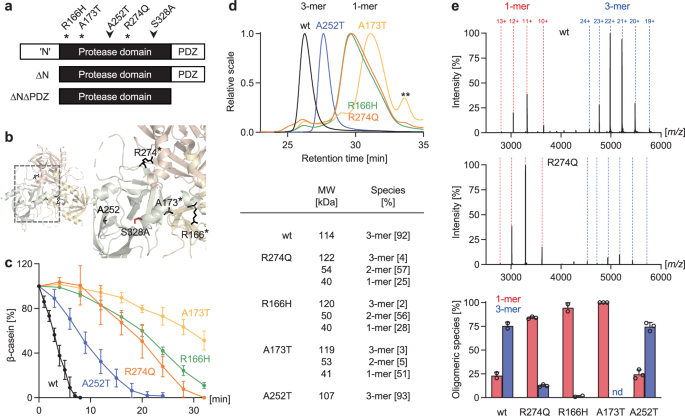
Loss-of-function mutations in the homotrimeric serine protease HTRA1 cause cerebral vasculopathy. Here, we establish independent approaches to achieve the functional correction of trimer assembly defects. Focusing on the prototypical R274Q mutation, we identify an HTRA1 variant that promotes trimer formation thus restoring enzymatic activity in vitro. Genetic experiments in Htra1R274Q mice further demonstrate that expression of this protein-based corrector in trans is sufficient to stabilize HtrA1-R274Q and restore the proteomic signature of the brain vasculature. An alternative approach employs supramolecular chemical ligands that shift the monomer-trimer equilibrium towards proteolytically active trimers. Moreover, we identify a peptidic ligand that activates HTRA1 monomers. Our findings open perspectives for tailored protein repair strategies.