2024-08-06 ヒューストン大学(UH)
<関連情報>
- https://uh.edu/news-events/stories/2024/august/08062024-varadarajan-nanosting-rx-and-vaccine.php
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-50133-2
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-50234-y
多抗原経鼻ワクチンはサルベドウイルスのチャレンジから保護し、ハムスターの感染を防ぐ Multi-antigen intranasal vaccine protects against challenge with sarbecoviruses and prevents transmission in hamsters
Ankita Leekha,Arash Saeedi,K M Samiur Rahman Sefat,Monish Kumar,Melisa Martinez-Paniagua,Adrian Damian,Rohan Kulkarni,Kate Reichel,Ali Rezvan,Shalaleh Masoumi,Xinli Liu,Laurence J. N. Cooper,Manu Sebastian,Courtney M. Sands,Vallabh E. Das,Nimesh B. Patel,Brett Hurst & Navin Varadarajan
Nature Communications Published:23 July 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-50133-2
Abstract
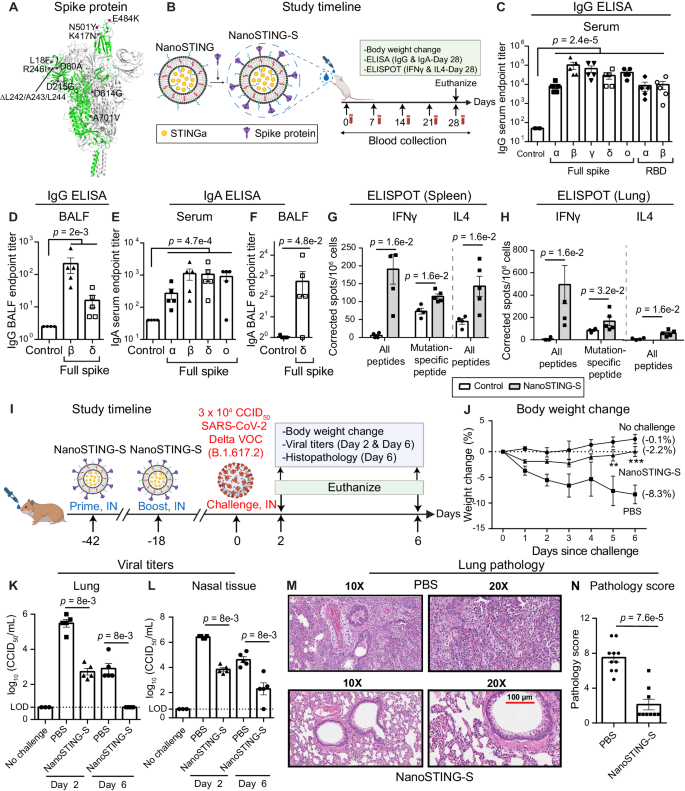
Immunization programs against SARS-CoV-2 with commercial intramuscular vaccines prevent disease but are less efficient in preventing infections. Mucosal vaccines can provide improved protection against transmission, ideally for different variants of concern (VOCs) and related sarbecoviruses. Here, we report a multi-antigen, intranasal vaccine, NanoSTING-SN (NanoSTING-Spike-Nucleocapsid), eliminates virus replication in both the lungs and the nostrils upon challenge with the pathogenic SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC. We further demonstrate that NanoSTING-SN prevents transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron VOC (BA.5) to vaccine-naïve hamsters. To evaluate protection against other sarbecoviruses, we immunized mice with NanoSTING-SN. We showed that immunization affords protection against SARS-CoV, leading to protection from weight loss and 100% survival in mice. In non-human primates, animals immunized with NanoSTING-SN show durable serum IgG responses (6 months) and nasal wash IgA responses cross-reactive to SARS-CoV-2 (XBB1.5), SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV antigens. These observations have two implications: (1) mucosal multi-antigen vaccines present a pathway to reducing transmission of respiratory viruses, and (2) eliciting immunity against multiple antigens can be advantageous in engineering pan-sarbecovirus vaccines.
経鼻ナノ粒子STINGアゴニストが動物モデルで呼吸器ウイルスを防御する An intranasal nanoparticle STING agonist protects against respiratory viruses in animal models
Ankita Leekha,Arash Saeedi,Monish Kumar,K. M. Samiur Rahman Sefat,Melisa Martinez-Paniagua,Hui Meng,Mohsen Fathi,Rohan Kulkarni,Kate Reichel,Sujit Biswas,Daphne Tsitoura,Xinli Liu,Laurence J. N. Cooper,Courtney M. Sands,Vallabh E. Das,Manu Sebastian,Brett L. Hurst & Navin Varadarajan
Nature Communications Published:18 July 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-50234-y
Abstract
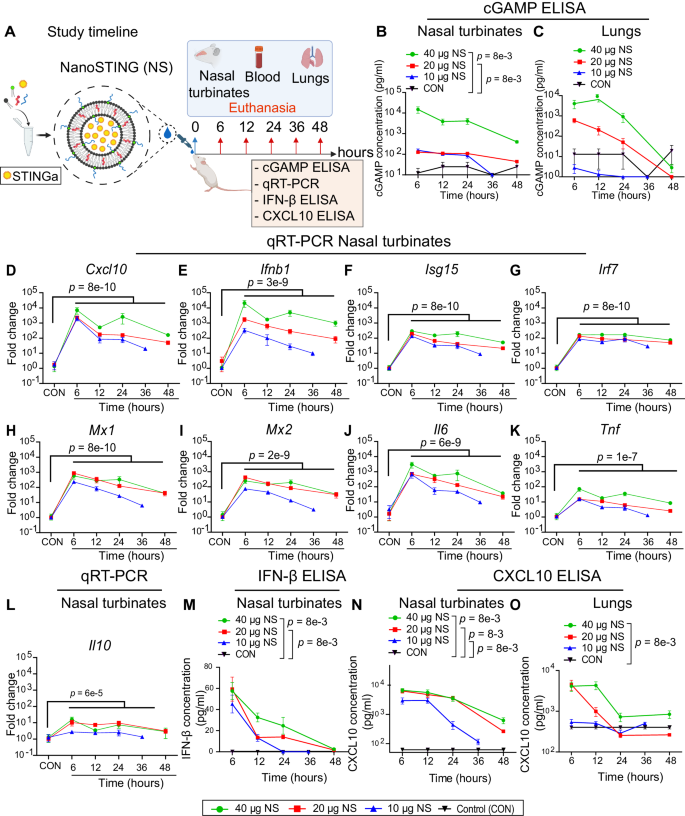
Respiratory viral infections cause morbidity and mortality worldwide. Despite the success of vaccines, vaccination efficacy is weakened by the rapid emergence of viral variants with immunoevasive properties. The development of an off-the-shelf, effective, and safe therapy against respiratory viral infections is thus desirable. Here, we develop NanoSTING, a nanoparticle formulation of the endogenous STING agonist, 2′-3′ cGAMP, to function as an immune activator and demonstrate its safety in mice and rats. A single intranasal dose of NanoSTING protects against pathogenic strains of SARS-CoV-2 (alpha and delta VOC) in hamsters. In transmission experiments, NanoSTING reduces the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron VOC to naïve hamsters. NanoSTING also protects against oseltamivir-sensitive and oseltamivir-resistant strains of influenza in mice. Mechanistically, NanoSTING upregulates locoregional interferon-dependent and interferon-independent pathways in mice, hamsters, as well as non-human primates. Our results thus implicate NanoSTING as a broad-spectrum immune activator for controlling respiratory virus infection.