2024-10-16 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)


<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/study-breast-cancer-drug-shows-potential-for-rare-appendix-cancer
- https://ascopubs.org/doi/10.1200/JCO.24.00511
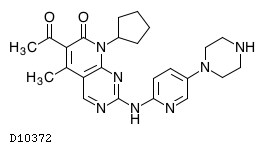
- https://oncolo.jp/news/palbociclib
GNAS変異を有する腹膜粘液癌腫症に対する新規治療としてのサイクリン依存性キナーゼ4/6阻害薬 Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibition as a Novel Therapy for Peritoneal Mucinous Carcinomatosis With GNAS Mutations
Jonathan Weitz, PhD, Daisuke Nishizaki, MD, Joy Liau, MD, Jay Patel, BS, Isabella Ng, BS, Siming Sun, BS, Dana Ramms, PhD, …, and Andrew M. Lowy, MD
Journal of Clinical Oncology Published:October 16, 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.24.00511
Abstract
Purpose
Mucinous neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract are characterized by a propensity for metastasis to the peritoneum, resulting in peritoneal mucinous carcinomatosis (PMC). A subset of these tumors, most often originating in the appendix, harbor mutations in the GNAS oncogene. While the natural history of GNAS-mutant PMC varies, patient outcomes are generally poor, as is response to cytotoxic chemotherapy. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical efficacy of single-agent palbociclib, a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)4/6 inhibitor, in patients with GNAS-mutant PMC.
Patients and Methods
We enrolled 16 patients with PMC in a single-arm personalized cancer therapy trial. For all patients, tumor tissue and/or circulating tumor DNA genomic profiling using next-generation sequencing and, when possible, PD-L1 expression, tumor mutational burden, and microsatellite instability status was assessed. Twelve of 16 patients had previous disease progression on at least one previous line of chemotherapy. The primary tumor was appendix in 13 patients, unknown in two patients, and pancreas in one patient. Eleven cases were classified as low grade, and five as high grade.
Results
In 13 of 16 patients, we observed a decrease in carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), and in six patients, the CEA declined by >50%. As measured by clinical and modified peritoneal RECIST criteria, 50% of evaluable patients had stable disease after 12 months of palbociclib. At a median follow-up of 17.6 months, median survival has not been reached. Clinical response to CDK4/6 inhibition was mirrored in tumors with GNAS mutation and mucinous histology using an ex vivo preclinical platform.
Conclusion
CDK4/6 inhibition with palbociclib had clinical activity in PMC characterized by mutations in GNAS that was superior to that previously reported with cytotoxic chemotherapy. CDK4/6 inhibition is a novel therapeutic strategy worthy of further evaluation in this subgroup of gastrointestinal neoplasms.