2024-12-04 ワシントン大学セントルイス校
<関連情報>
- https://source.washu.edu/2024/12/research-reveals-how-fructose-in-diet-enhances-tumor-growth/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-08258-3
食餌性フルクトースは臓器間脂質移行を介して間接的に腫瘍の成長を促進する Dietary fructose enhances tumour growth indirectly via interorgan lipid transfer
Ronald Fowle-Grider,Joe L. Rowles III,Isabel Shen,Yahui Wang,Michaela Schwaiger-Haber,Alden J. Dunham,Kay Jayachandran,Matthew Inkman,Michael Zahner,Fuad J. Naser,Madelyn M. Jackstadt,Jonathan L. Spalding,Sarah Chiang,Kyle S. McCommis,Roland E. Dolle,Eva T. Kramer,Sarah M. Zimmerman,George P. Souroullas,Brian N. Finck,Leah P. Shriver,Charles K. Kaufman,Julie K. Schwarz,Jin Zhang &Gary J. Patti
Nature Published:04 December 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-08258-3
Abstract
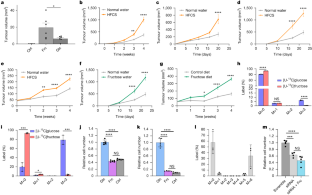
Fructose consumption has increased considerably over the past five decades, largely due to the widespread use of high-fructose corn syrup as a sweetener1. It has been proposed that fructose promotes the growth of some tumours directly by serving as a fuel2,3. Here we show that fructose supplementation enhances tumour growth in animal models of melanoma, breast cancer and cervical cancer without causing weight gain or insulin resistance. The cancer cells themselves were unable to use fructose readily as a nutrient because they did not express ketohexokinase-C (KHK-C). Primary hepatocytes did express KHK-C, resulting in fructolysis and the excretion of a variety of lipid species, including lysophosphatidylcholines (LPCs). In co-culture experiments, hepatocyte-derived LPCs were consumed by cancer cells and used to generate phosphatidylcholines, the major phospholipid of cell membranes. In vivo, supplementation with high-fructose corn syrup increased several LPC species by more than sevenfold in the serum. Administration of LPCs to mice was sufficient to increase tumour growth. Pharmacological inhibition of ketohexokinase had no direct effect on cancer cells, but it decreased circulating LPC levels and prevented fructose-mediated tumour growth in vivo. These findings reveal that fructose supplementation increases circulating nutrients such as LPCs, which can enhance tumour growth through a cell non-autonomous mechanism.


