2024-12-17 ロイヤルメルボルン工科大学(RMIT)
<関連情報>
- https://www.rmit.edu.au/news/all-news/2024/dec/blood-test
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.4c09919
- https://medibio.tiisys.com/134719/
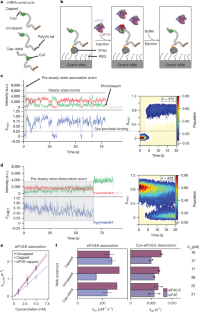
ヒト白血病血液における患者特異的ナノ粒子ターゲティング Patient-Specific Nanoparticle Targeting in Human Leukemia Blood
Yi Ju,Shiyao Li,Abigail Er Qi Tan,Emily H. Pilkington,Paul T. Brannon,Magdalena Plebanski,Jiwei Cui,Frank Caruso,Kristofer J. Thurecht,Constantine Tam,and Stephen J. Kent
ACS Nano Published: October 9, 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.4c09919
Abstract

Antibody-directed targeting of chemotherapeutic nanoparticles to primary human cancers holds promise for improving efficacy and reducing off-target toxicity. However, clinical responses to targeted nanomedicines are highly variable. Herein, we prepared and examined a matrix of 9 particles (organic and inorganic particles of three surface chemistries with and without antibody functionalization) and developed an ex vivo model to study the person-specific targeting of nanoparticles in whole blood of 15 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Generally, anti-CD20-functionalized poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) nanoparticles efficiently targeted CLL cells, leading to low off-target phagocytosis by granulocytes and monocytes in the blood. However, there was up to 164-fold patient-to-patient variability in the CLL targeting. This was further exemplified through using clinically relevant PEGylated doxorubicin-encapsulated liposomes, which showed high interpersonal differences in CLL targeting (up to 234-fold differences) and off-target phagocytosis (up to 65- and 112-fold differences in granulocytes and monocytes, respectively). Off-target phagocytosis led to almost all monocytes being killed within 24 h of treatment. Variance of the off-target association of PEGylated liposomes with granulocytes and monocytes significantly correlated to anti-PEG immunoglobulin G levels in the blood of CLL patients. A negative correlation between CLL targeting of PEG particles and anti-PEG immunoglobulin M levels was found in the blood. Taken together, our study identifies anti-PEG antibodies as key proteins in modulating patient-specific targeting of PEGylated nanoparticles in human leukemia blood. Other factors, such as the antigen expression of targeted cells and fouling properties of nanoparticles, also play an important role in patient-specific targeting. The human leukemia blood assay we developed provides an ex vivo model to evaluate interpersonal variances in response to targeted nanomedicines.