2025-02-05 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/materials-research-institute/story/new-smart-sensor-takes-pain-out-wound-monitoring
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-55790-x
熱電多孔質レーザー誘起グラフェンベースの歪み温度分離と自己発電センシング Thermoelectric porous laser-induced graphene-based strain-temperature decoupling and self-powered sensing
Li Yang,Xue Chen,Ankan Dutta,Hui Zhang,Zihan Wang,Mingyang Xin,Shuaijie Du,Guizhi Xu & Huanyu Cheng
Nature Communications Published:17 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55790-x
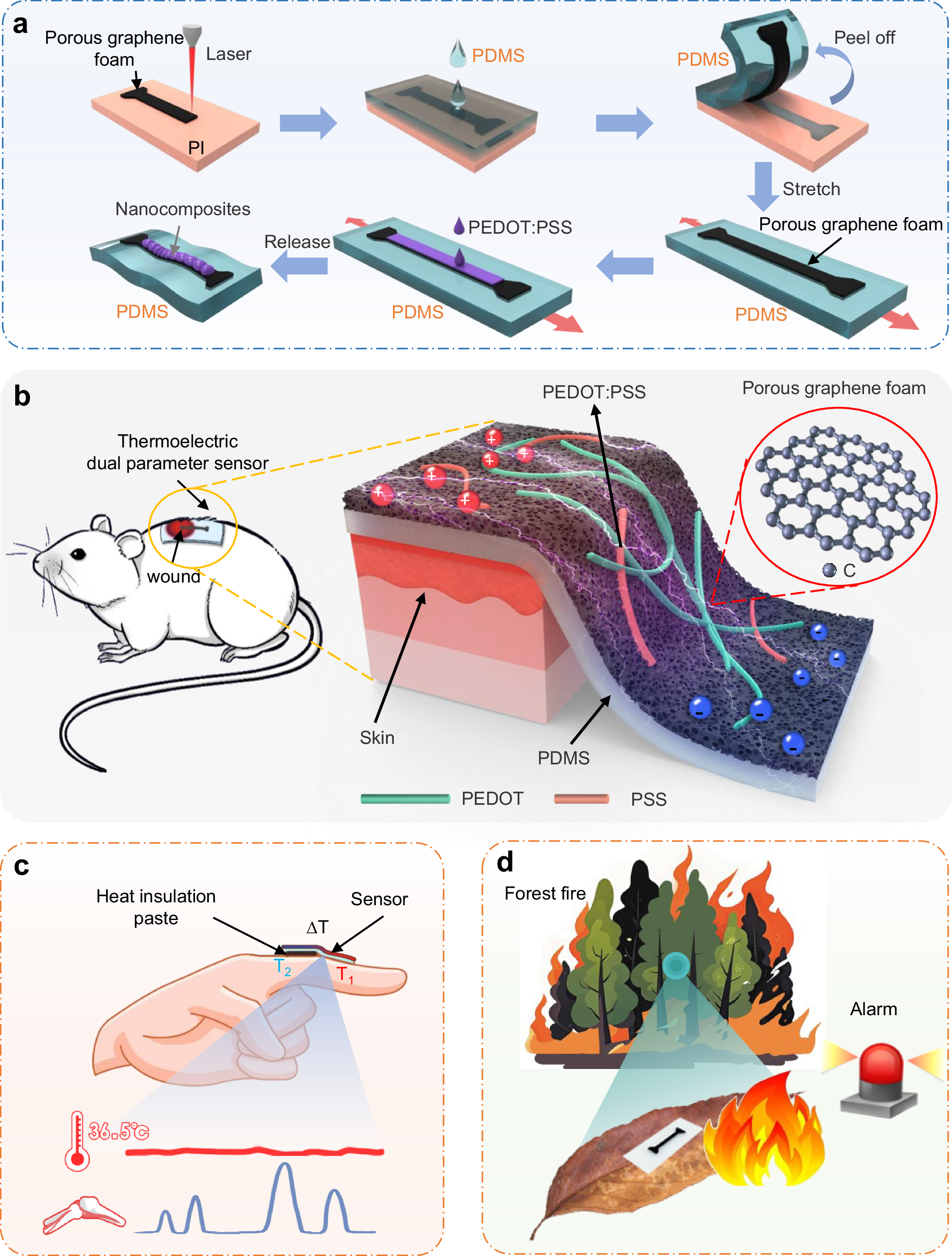
Abstract
Despite rapid developments of wearable self-powered sensors, it is still elusive to decouple the simultaneously applied multiple input signals. Herein, we report the design and demonstration of stretchable thermoelectric porous graphene foam-based materials via facile laser scribing for self-powered decoupled strain and temperature sensing. The resulting sensor can accurately detect temperature with a resolution of 0.5°C and strain with a gauge factor of 1401.5. The design of the nanocomposites also explores the synergistic effect between the porous graphene and thermoelectric components to greatly enhance the Seebeck coefficient by almost four times (from 9.703 to 37.33 μV/°C). Combined with the stretchability of 45%, the self-powered sensor platform allows for early fire detection in remote settings and accurate and decoupled monitoring of temperature and strain during the wound healing process in situ. The design concepts from this study could also be leveraged to prepare multimodal sensors with decoupled sensing capability for accurate multi-parameter detection towards health monitoring.