2025-04-15 清華大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.tsinghua.edu.cn/en/info/1245/14190.htm
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-025-07892-5
化学的および光誘導性cGAS活性化の機構的知見に基づく合理的デザイン Rational design of chemical- and light-inducible cGAS activation based on mechanistic insights
Yiting Tang,Wenjuan Wang & Chunlai Chen
Communications Biology Published:02 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-025-07892-5
Abstract
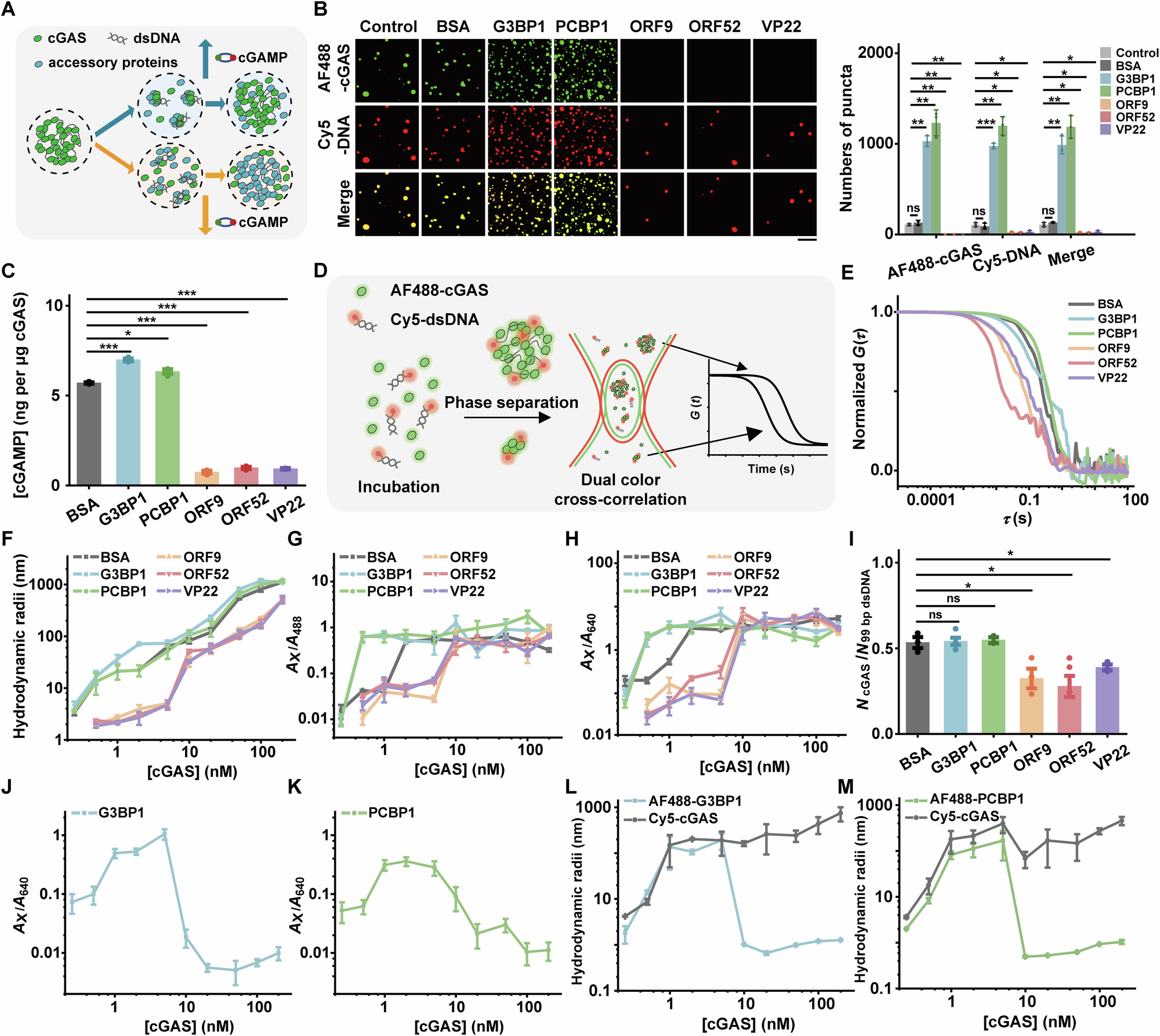
Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) plays a pivotal role in the cGAS-STING pathway as a DNA sensor that binds to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and subsequently induces type I interferon expression, thereby contributing significantly to the innate immune response. Several human and viral proteins have been identified to enhance or inhibit cGAS activity. The underlying molecular basis that underpins these regulatory effects remain elusive. In this study, we employ the highly sensitive dcFCCS method to systematically examine phase separation and binding affinities among cGAS, dsDNA, and several accessory proteins. We reveal that the binding strength between cGAS and accessory proteins is the key factor to affect cGAS phase separation and enzymatic activity, which guide us to develop a chemical-inducible strategy and a light-inducible strategy to manipulate cGAS phase separation and immune signaling in test tubes and in living cells. Thus, our mechanistic insights offer guidance for manipulating multi-component phase separation systems.