2025-04-17 慶應義塾大学
<関連情報>
- https://news.nifty.com/article/economy/business/12365-4027252/
- https://www.keio.ac.jp/ja/press-releases/files/2025/4/17/250417-1.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08861-y
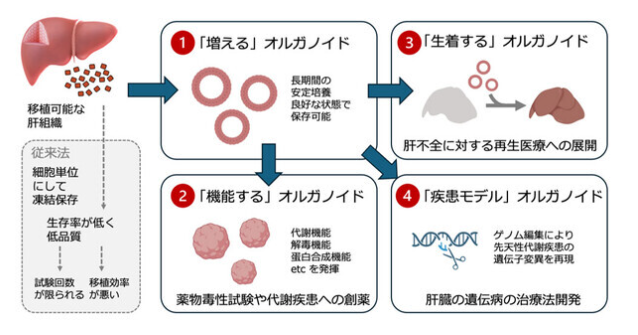
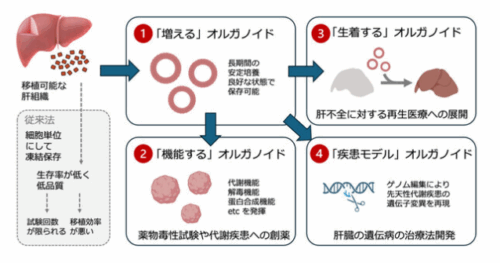
代謝機能を有するヒト成体肝細胞オルガノイドの作製 Generation of human adult hepatocyte organoids with metabolic functions
Ryo Igarashi,Mayumi Oda,Ryo Okada,Tomoki Yano,Sirirat Takahashi,Strahil Pastuhov,Mami Matano,Norio Masuda,Kazuhiro Togasaki,Yuki Ohta,Saeko Sato,Takako Hishiki,Makoto Suematsu,Manabu Itoh,Masayuki Fujii & Toshiro Sato
Nature Published:16 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-08861-y
Abstract
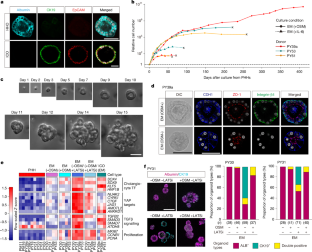
Proliferating hepatocytes often undergo ductal metaplasia to balance the energy trade-off between cellular functions and replication, hindering the expansion of human adult hepatocytes with functional competency1. Here we demonstrate that the combined activation of Wnt and STAT3 signalling enables long-term self-renewal of human adult hepatocyte organoids. YAP activation facilitates hepatocyte proliferation but commits it towards the biliary duct lineage. By contrast, STAT3 activation by oncostatin M induces hepatocyte proliferation while counteracting ductal metaplasia and maintaining the hepatic identity. Xenotransplanted hepatocyte organoids repopulate the recipient mouse liver and reconstitute the metabolic zonation structure. Upon niche factor removal and hormone supplementation, hepatocyte organoids form cord-like structures with bile canalicular networks and exhibit major liver metabolic functions comparable to those of in vivo hepatocytes. Hepatocyte organoids are amenable to gene editing, prompting functional modelling of inherent metabolic liver diseases. The new culture system offers a promising avenue for developing therapeutic strategies against human liver diseases.