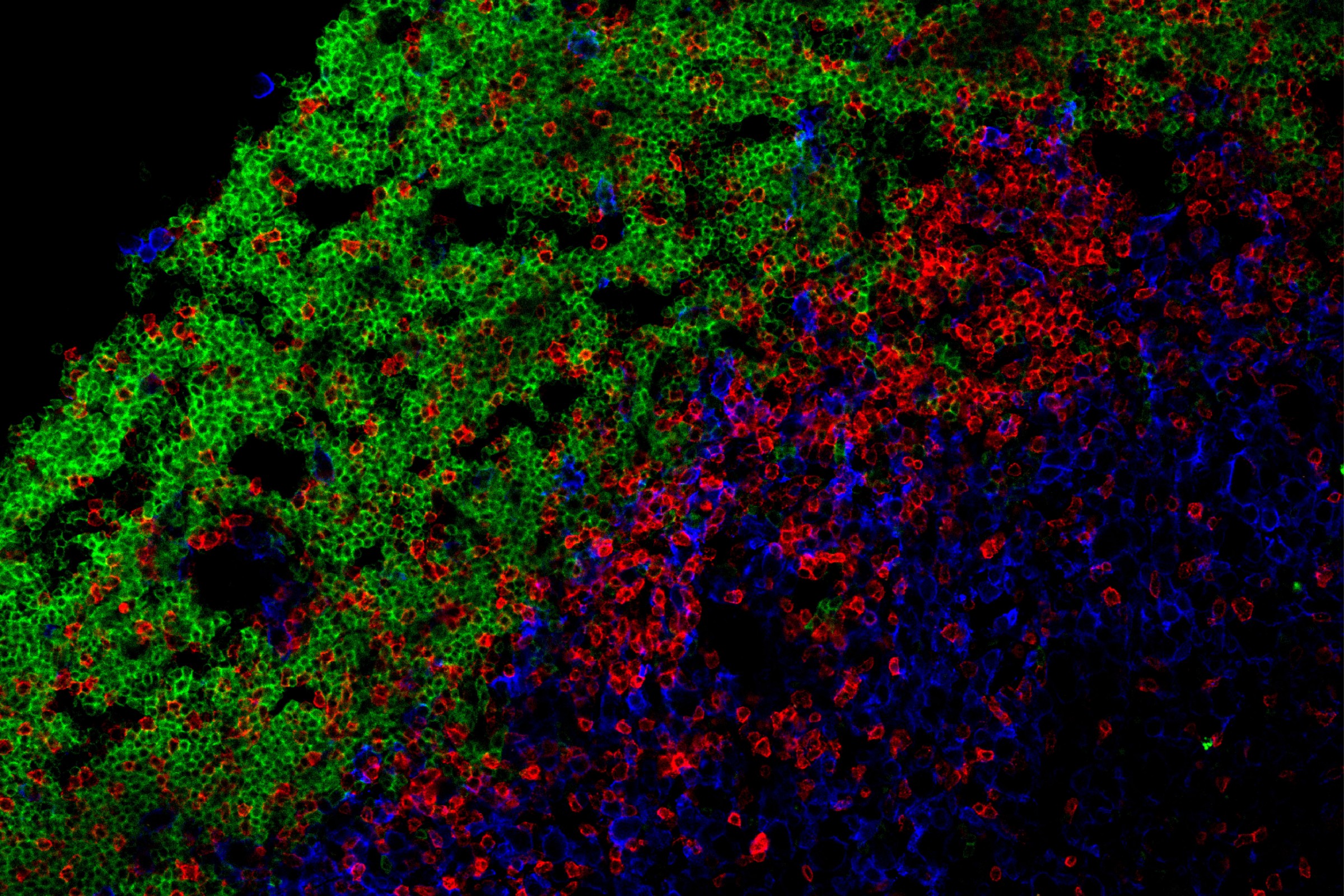
2025-04-25 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
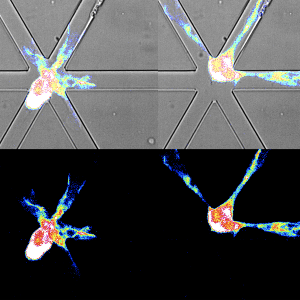
Pretty tight: Cells under mechanical stress. Capture: Renkawitz Group
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/cell-biology-how-cells-protect-their-centrosome-against-mechanical-forces.html
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adx4047
中心体を破壊から守ることで効率的な細胞ナビゲーションが可能になる Protecting centrosomes from fracturing enables efficient cell navigation
Madeleine T. Schmitt, Janina Kroll, Mauricio J. A. Ruiz-Fernandez, Robert Hauschild, […] , and Jörg Renkawitz
Science Advances Published:25 Apr 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adx4047
Abstract
The centrosome is a microtubule orchestrator, nucleating and anchoring microtubules that grow radially and exert forces on cargos. At the same time, mechanical stresses from the microenvironment and cellular shape changes compress and bend microtubules. Yet, centrosomes are membraneless organelles, raising the question of how centrosomes withstand mechanical forces. Here, we discover that centrosomes can deform and even fracture. We reveal that centrosomes experience deformations during navigational pathfinding within motile cells. Coherence of the centrosome is maintained by Dyrk3 and cNAP1, preventing fracturing by forces. While cells can compensate for the depletion of centriolar-based centrosomes, the fracturing of centrosomes impedes cellular function by generating coexisting microtubule organizing centers that compete during path navigation and thereby cause cellular entanglement in the microenvironment. Our findings show that cells actively maintain the integrity of the centrosome to withstand mechanical forces. These results suggest that centrosome stability preservation is fundamental, given that almost all cells in multicellular organisms experience forces.