2025-05-01 北海道大学,北海道科学大学
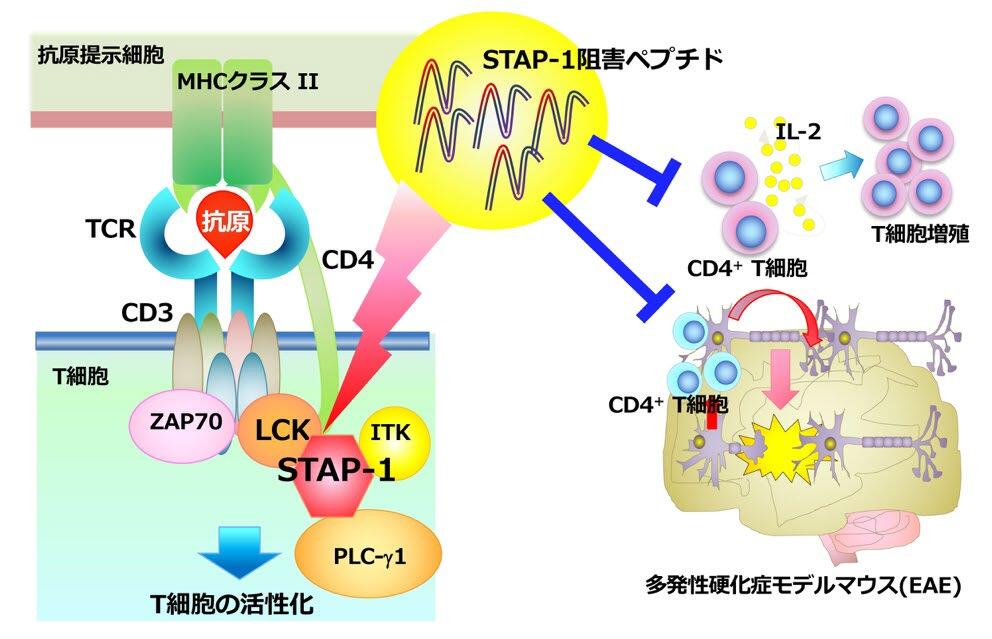 本研究による新たな自己免疫疾患治療戦略
本研究による新たな自己免疫疾患治療戦略
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/2025/05/t-5.html
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/250501_pr2.pdf
- https://academic.oup.com/immunohorizons/article/9/6/vlaf015/8120671
STAP-1由来のペプチドはSTAP-1-LCK結合を阻害することでTCR誘導性T細胞活性化と免疫疾患を抑制する STAP-1-derived peptide suppresses TCR-mediated T cell activation and ameliorates immune diseases by inhibiting STAP-1–LCK binding
Yuto Sasaki, Kota Kagohashi, Shoya Kawahara, Yuichi Kitai, Ryuta Muromoto, Kenji Oritani, Jun-Ichi Kashiwakura, Tadashi Matsuda
ImmunoHorizons Published:27 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/immhor/vlaf015
Abstract
Signal-transducing adaptor protein-1 (STAP-1) is an adaptor protein specifically expressed in immune cells, such as T cells. We previously demonstrated that STAP-1 positively upregulates T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated T cell activation by interacting with LCK and phospholipase C-γ1 and affecting autoimmune demyelination and airway inflammation. In this study, we aimed to generate a new STAP-1-derived peptide, iSP1, to inhibit the STAP-1–LCK interaction. We also analyzed its function in vitro and in vivo. iSP1 successfully interfered with STAP-1–LCK binding and suppressed TCR-mediated signal transduction, interleukin-2 production, and human and murine T cell proliferation. Additionally, iSP1 prevented the progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting Th1 and Th17 cell infiltration. Our findings suggest iSP1 as a new therapeutic immunomodulatory agent for T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases.