2025-05-20 北海道⼤学
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/250520_news_press.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772610X25000212
神経芽腫および骨肉腫に対する抗GD2抗体を用いた近赤外光免疫療法 Near-infrared photoimmunotherapy using antiGD2 antibody for neuroblastoma and osteosarcoma
Jimei Zhao, Kohei Nakajima, Masahiro Ueki, Yukayo Terashita, Shinsuke Hirabayashi, Yuko Cho, Mikako Ogawa, Atsushi Manabe
EJC Paediatric Oncology Available online: 5 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcped.2025.100233
Highlights
- Near-infrared photoimmunotherapy(NIR-PIT): novel treatment specific to cancer antigen.
- A preclinical study about NIR-PIT for pediatric cancer.
- NIR-PIT with antiGD2 antibody was effective for neuroblastoma and osteosarcoma cell.
- NIR-PIT with antiGD2 antibody was suggested to be effective for neuroblastoma mice model.
Abstract
Introduction
Near-infrared photoimmunotherapy (NIR-PIT) is a novel cancer therapy that specifically targets cancer cells. In NIR-PIT, antibody-photo-absorber-conjugates (APCs), specific for cancer antigens, target cancer cells. APCs that bind to antigens and are irradiated with NIR-light kill targeted cells. NIR-PIT has been clinically applied to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in Japan, but not to pediatric cancers. Generally, neuroblastoma and osteosarcoma express disialoganglioside (GD2), making NIR-PIT that targets GD2 an additional treatment option.
Methods
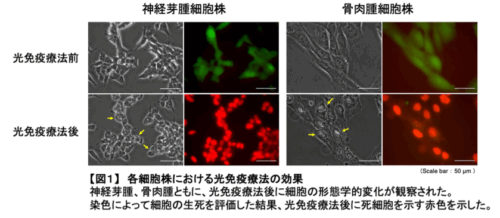
Antihuman GD2 monoclonal antibody (clone 3F8) was conjugated with photo-absorber, IRDyeⓇ 700DX (IR700). A human neuroblastoma cell (SK-N-SH) was used for in vitro and in vivo experiments, whereas human osteosarcoma cells (NOS-10, MG-63) were utilized for in vitro experiments. Microscopy and flow cytometry were used to evaluate cell death after NIR-PIT, and longitudinal measurement of tumor size and histological observation were utilized to assess the effect of NIR-PIT on the xenograft model.
Results
EthD-1 staining after NIR-PIT confirmed the morphological changes (swelling and bleb formation) observed by microscopy and cell death. Flow cytometry verified the significant increase in dead cells after NIR-PIT. Tumor growth in the mice model was significantly inhibited at day 10 of the experiment and destroyed tumor tissue was histologically observed in the PIT-treated mice.
Conclusion
The efficacy of NIR-PIT with antiGD2 antibody for neuroblastoma and osteosarcoma was indicated. Additionally, NIR-PIT efficacy against neuroblastoma was indicated by the mice model in vivo. Therefore, further experiments and more effective protocols should be considered for clinical application.