2025-06-07 東京科学大学
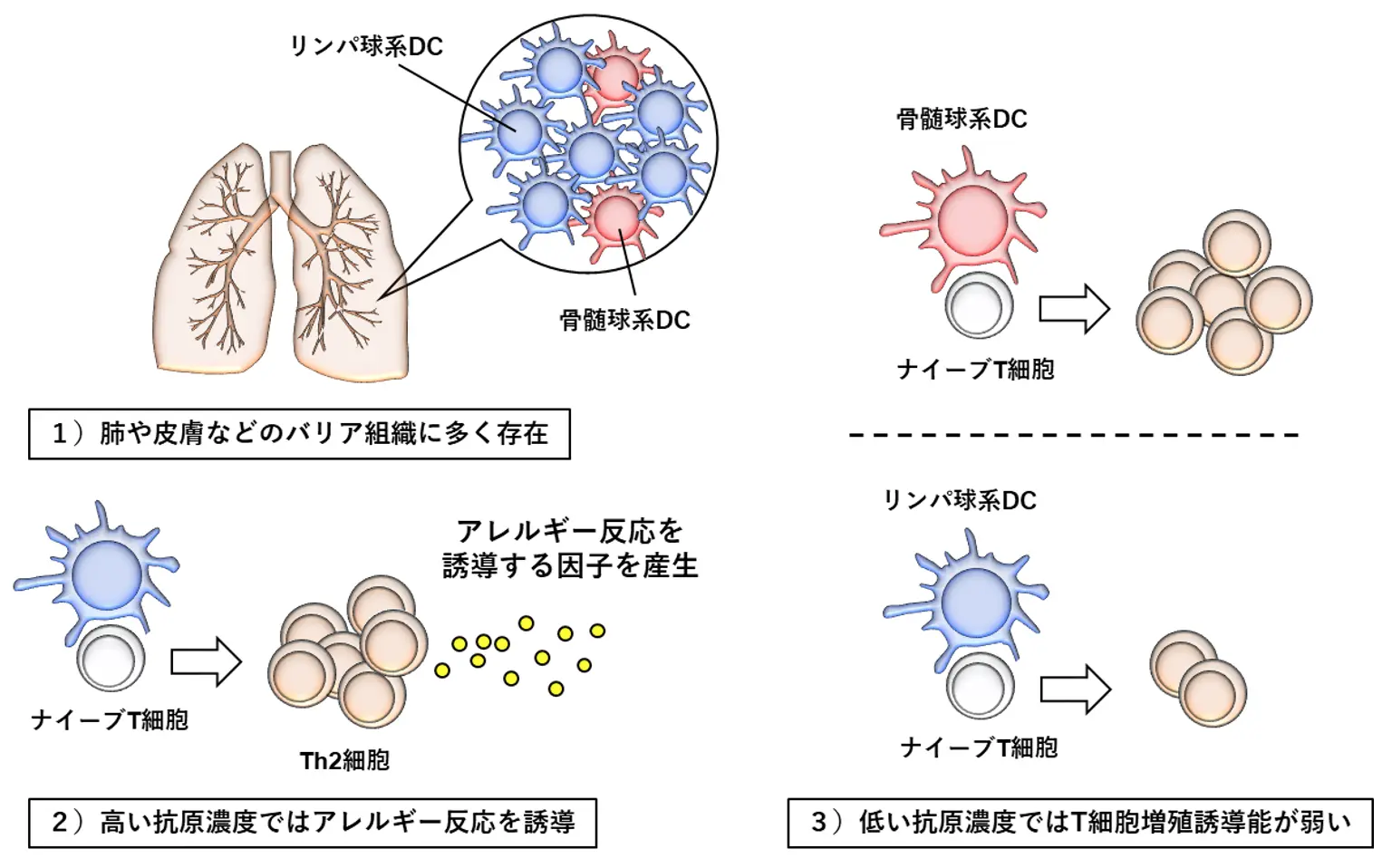
図1. リンパ球系DCの特徴
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/lrxa26apwk83
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=1735&prevId=&key=89273927896dcc6938fd6db554899884.pdf
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adt4909
異なる組織分布と機能を持つ従来の樹状リンパ球の多様な発生経路 Diverse developmental pathways of lymphoid conventional dendritic cells with distinct tissue distribution and function
Masashi Kanayama, Yuta Izumi, Nobuyuki Onai, Takako Akashi, […] , and Toshiaki Ohteki
Science Advances Published:6 Jun 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adt4909
Abstract
Conventional dendritic cells (cDCs) regulate adaptive immunity. Although most cDCs are of myeloid origin (M-cDCs), some cDCs originate from pro–plasmacytoid DCs (pro-pDCs) via pDC-like cells [lymphoid cDCs (L-cDCs)]. Using lymphoid progenitor–tracking systems, we report tissue segregation, a unique differentiation pathway, and the functions of L-cDCs. Notably, L-cDC2s are predominantly distributed in barrier tissues such as the lungs and skin. Single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis revealed the enrichment of lymphocyte signature genes in L-cDCs. We identified lymphocyte-primed cDC precursors, which are distinct from pDC-like cells, as sources of L-cDCs. Compared with M-cDC2s, L-cDC2s weakly primed T cells under low-dose antigen stimulation and preferentially promoted T helper 2 (TH2) differentiation under sufficient antigenic stimulation. These results suggest the diverse developmental pathways of L-cDCs and imply the contribution of L-cDCs to tolerance and hyperresponses to TH2-related antigens in barrier tissues.