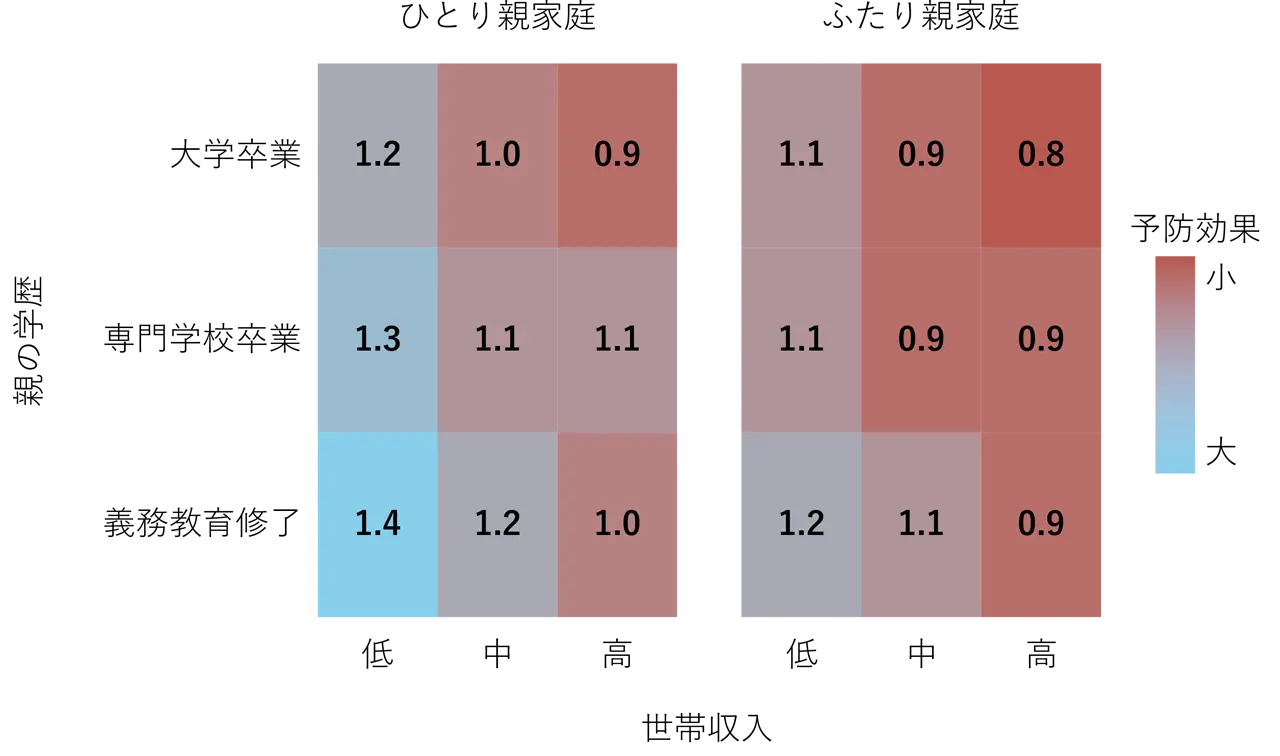
2025-07-02 理化学研究所
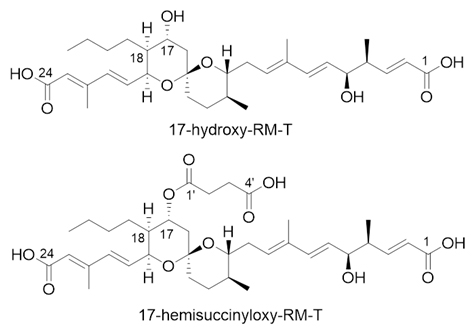
二つの新規RM誘導体の構造
<関連情報>
- https://www.riken.jp/press/2025/20250702_1/index.html
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2025/sc/d5sc01355k
チトクロームP450revIの位置選択性を変化させたレベロマイシン誘導体の生合成 Biosynthesis of reveromycin derivatives by altering the regioselectivity of cytochrome P450revI
Ya Fen Yong, Song Liu, Katsuyuki Sakai, Keisuke Fujiyama, Hiroshi Takagi,Yushi Futamura, Takeshi Shimizu, Hiroyuki Osada, Eugene Boon Beng Ong and Shunji Takahashi
Chemical Science Published:23 Jun 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1039/D5SC01355K
Abstract
Reveromycin A (RM-A) (1) has a 6,6-spiroacetal core structure that is important for its biological activity. However, 1 undergoes a spiroacetal rearrangement to form RM-B (2) with a 5,6-spiroacetal core, which exhibits reduced bioactivity. This undesired rearrangement is partly due to the hemisuccinate moiety at the C18 position of 1. In 1 biosynthesis, P450revI catalyses the C18-hydroxylation of RM-T (3), which is essential for its subsequent hemisuccinylation to generate 1. In this study, we aimed to alter the P450revI regioselectivity to improve the stability of the 6,6-spiroacetal core and expand the structural diversity of RMs. Candidate amino acid residues for mutagenesis studies were selected by comparing the co-crystal structure of P450revI with the docking models of the P450revI mutant-3 complexes. Notably, the P450revI-A241L mutant selectively produced novel RM derivatives. Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis revealed that P450revI-A241L catalysed the C17-hydroxylation of 3 to produce 17-hydroxy-RM-T (6). Co-crystal structure analysis of the P450revI-A241L-3 complex revealed that the pro-R hydrogen at the C17 position faces toward the haem iron. Introduction of the P450revI-A241L mutant gene into the Actinacidiphila reveromycinica SN-593-ΔrevI strain led to the production of 17-hemisuccinyloxy-RM-T (7). After the successful bioproduction of RM derivatives, we evaluated their structural stabilities and biological activities. Compounds 6 and 7 exhibited better stabilities than 18-hydroxylated-3 (RM-T1; 4) and 1, respectively. Biological activity analysis revealed that 6 and 7 exhibited anti-malarial and anti-multiple myeloma activities, respectively, comparable to those of 1 and 3, while showing low cytotoxicity against human cell lines. Overall, this study highlights the potential of RM derivatives as pharmaceuticals.