2025-07-22 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)
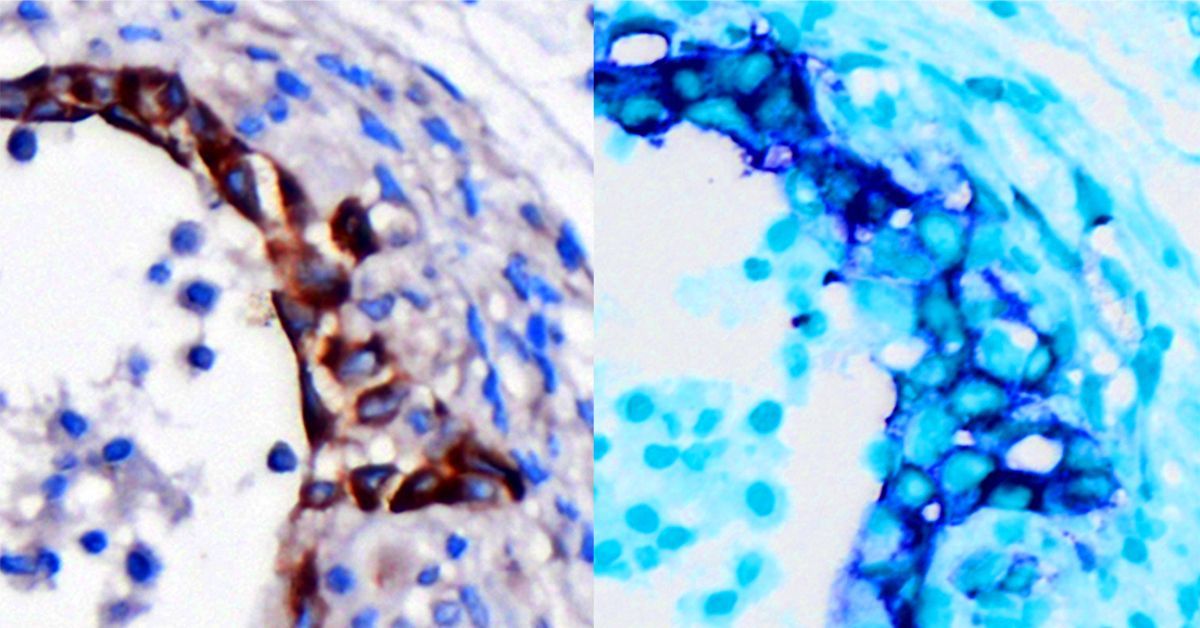
On the left are pancreas cells showing early stages of malignant cancer in brown. On the right, the same cells stained blue indicate they are Integrin β3 (ITGB3) positive. Photo Credit: UC San Diego Health Sciences
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/gene-signature-an-early-warning-system-for-aggressive-pancreatic-cancer-study-finds
- https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(25)00781-8
STAT3/インテグリン軸が膵臓癌の発生と進行を加速する A STAT3/integrin axis accelerates pancreatic cancer initiation and progression
Alejandro D. Campos ∙ Ryan M. Shepard ∙ Zachary Ortega ∙ … ∙ Hiromi I. Wettersten, ∙ Sara M. Weis ∙ David A. Cheresh
Cell Reports Published:July 22, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116010
Highlights
- Integrin β3 is a STAT3-regulated stress/inflammatory response gene
- The STAT3/β3 axis accelerates tumor initiation and promotes the basal PDAC subtype
- Accessibility of enhancer regions to STAT3 controls the expression of integrin β3
- STAT3-receptive enhancers identify patient tumors adapting to stress and inflammation
Summary
The signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathway drives pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) progression by coordinating cellular responses to stress and inflammation. We perform ChIP-seq on hypoxia- or oncostatin-M-treated PDAC cells to identify sites at which phospho-STAT3 binds to regulate the expression of genes linked to poor survival. A top hit among these is ITGB3, which we show promotes PDAC initiation and progression. Single-cell transcriptomics reveal that ITGB3 expression is enriched in PDAC cells experiencing oxidative stress due to chemotherapy. Moreover, high ITGB3 expression positively correlates with STAT3 signaling, hypoxia, and the basal subtype. Mechanistically, chromatin accessibility at ITGB3 enhancers controls STAT3’s ability to induce ITGB3 expression, illuminating a plastic regulatory mechanism modulating STAT3 activity. Leveraging this insight, we identify additional STAT3 target genes regulated similarly to ITGB3 to establish an 18-gene signature involved in adaptive responses and able to stratify survival outcomes. Collectively, these findings highlight a novel opportunity to stratify PDAC subpopulations for STAT3-targeted therapies.