2025-08-17 北京大学(PKU)
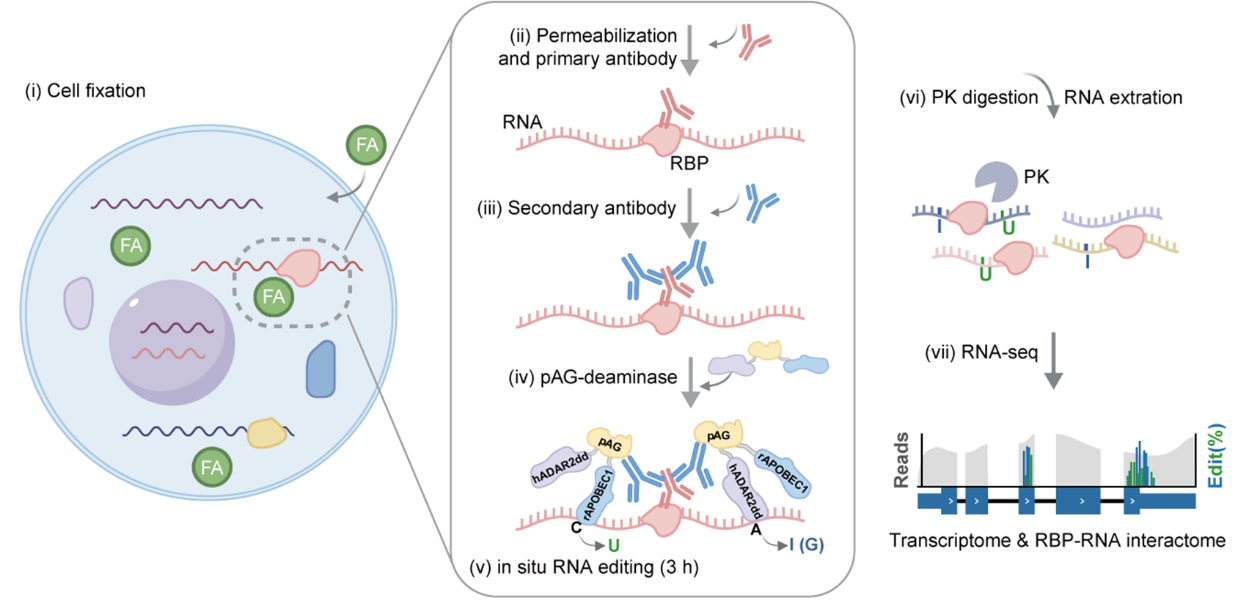
Figure 1. Schematics of MAPIT-seq
<関連情報>
- https://newsen.pku.edu.cn/news_events/news/research/15058.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-025-02774-4
単一細胞・組織におけるin situ RNA-タンパク質相互作用とトランスクリプトームの同時プロファイリング Co-profiling of in situ RNA-protein interactions and transcriptome in single cells and tissues
Qi-Xuan Cheng,Gang Xie,Xiangyu Zhang,Jie Wang,Shuangjin Ding,Yi-Xia Wu,Ming Shi,Fei-Fei Duan,Zi-Li Wan,Jing-Jia Wei,Junyu Xiao & Yangming Wang
Nature Methods Published:11 August 2025
DOIh:ttps://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-025-02774-4
Abstract
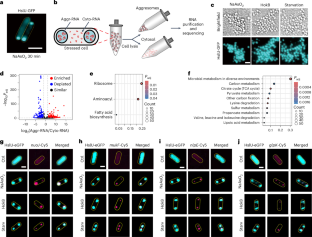
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are essential regulators of RNA fate and function. A long-standing challenge in studying RBP regulation has been mapping RNA interactomes within the dynamic transcriptomic landscape, especially in single-cell contexts and primary tissues. Here we introduce MAPIT-seq (modification added to RBP interacting transcript-sequencing), which uses an antibody-directed editing strategy to map genome-wide in situ RBP–RNA interactions and gene expression concurrently. We demonstrate MAPIT-seq’s robustness across multiple RBPs and systematically analyze RNA substrates associated with core polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) components. MAPIT-seq is also applicable to frozen tissue sections, enabling the mapping of RBP roles during brain development. Importantly, we develop high-throughput single-cell MAPIT-seq (scMAPIT-seq) to reveal cell stage-specific RBP regulation. In summary, MAPIT-seq expands multi-omics profiling, providing an effective framework to study post-transcriptional regulation in dynamic biological processes and clinically relevant scenarios.