2025-09-30 イェール大学
<関連情報>
- https://news.yale.edu/2025/09/30/unraveling-painful-mystery-protein-plays-key-role-modulating-pain-response
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-63767-7
カルモジュリン結合はカルシウムを介したTRPA1脱感作に必要である Calmodulin binding is required for calcium mediated TRPA1 desensitization
Justin H. Sanders,Camila Garcia,Kehinde M. Taiwo,Gregory Quevedo,Glory A. Adekanye,Avnika Bali & Candice E. Paulsen
Nature Communications Published:30 September 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-63767-7
Abstract
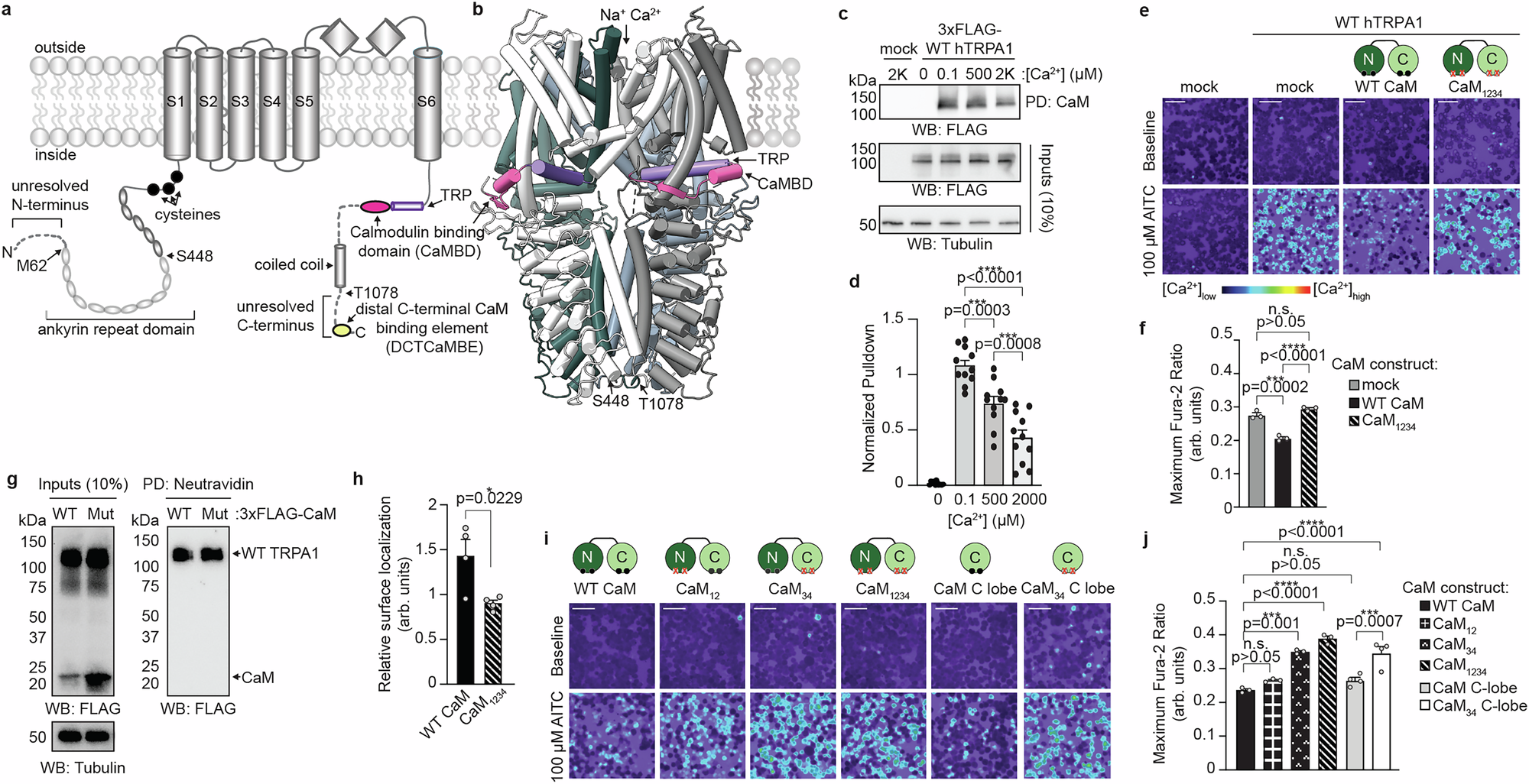
TRPA1 is an essential calcium (Ca2+)-permeable channel involved in nociception and inflammation. It exhibits complex and mechanistically elusive Ca2+ regulation with initial potentiation then rapid desensitization. We find that the universal Ca2+ sensor Calmodulin (CaM) binds TRPA1 in cells at rest and suppresses channel activity. Combining biochemical, biophysical, modeling, NMR spectroscopy, and functional approaches, we identify an evolutionarily conserved, high-affinity Ca2+/CaM binding element in the TRPA1 distal C-terminus. Genetic or biochemical perturbation of Ca2+/CaM binding to this site yields hyperactive channels that exhibit drastic slowing of desensitization with minor effect on potentiation. Higher extracellular Ca2+ partially rescues slowed desensitization. Our results identify a critical regulatory element in an unstructured TRPA1 region highlighting the importance of these domains, they reveal Ca2+/CaM is an essential TRPA1 auxiliary subunit required for proper channel function, and they suggest that Ca2+/CaM binding at this distal site stabilizes a long-range allosteric mechanism to drive rapid desensitization.