2025-10-29 マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
Web要約 の発言:
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2025/your-brain-without-sleep-1029
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-025-02098-8
睡眠不足後の注意力低下は、神経血管、瞳孔、脳脊髄液の流動ダイナミクスの連携に起因する Attentional failures after sleep deprivation are locked to joint neurovascular, pupil and cerebrospinal fluid flow dynamics
Zinong Yang,Stephanie D. Williams,Ewa Beldzik,Stephanie Anakwe,Emilia Schimmelpfennig & Laura D. Lewis
Nature Communications Published:29 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-025-02098-8
Abstract
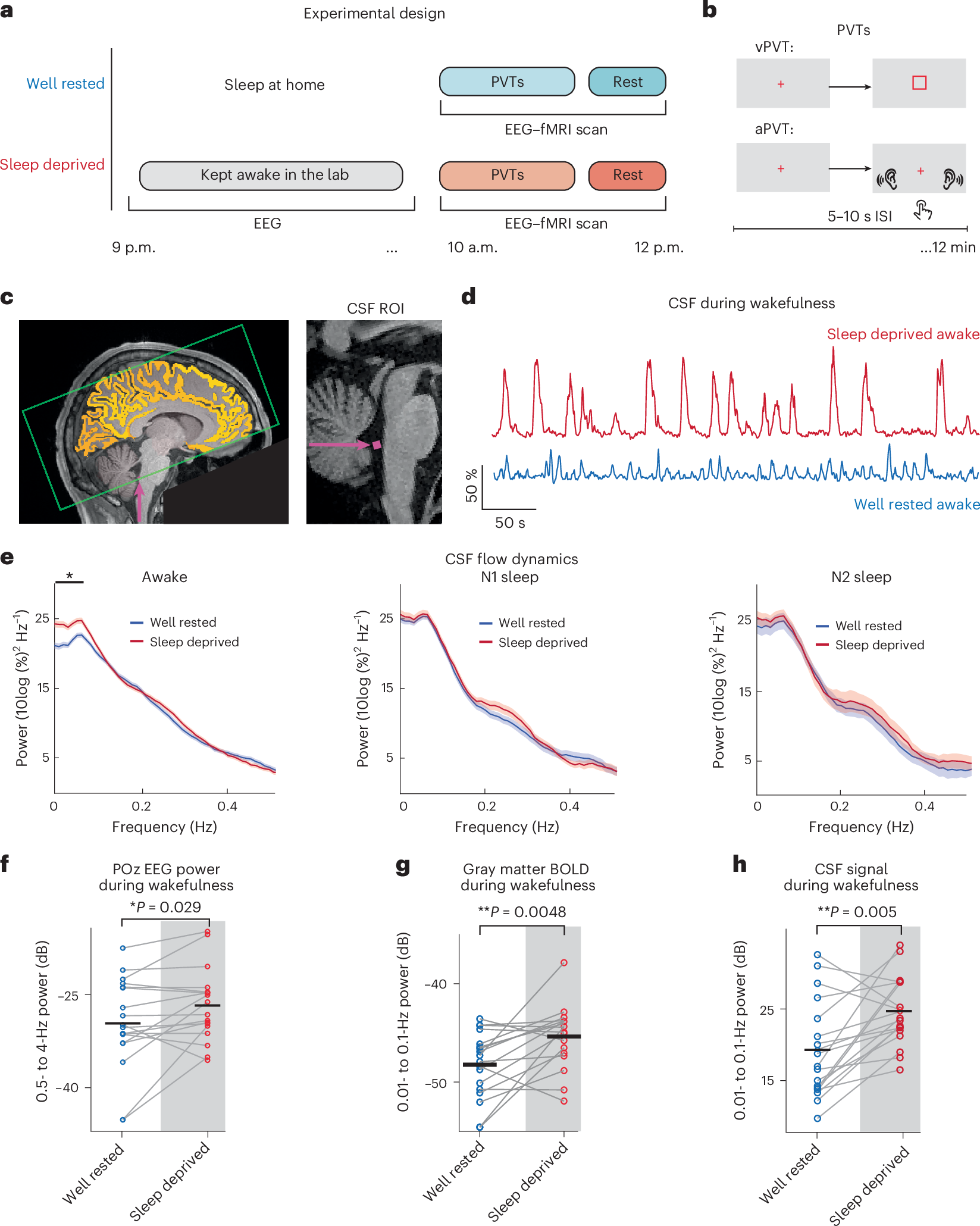
Sleep deprivation rapidly disrupts cognitive function and in the long term contributes to neurological disease. Why sleep deprivation has such profound effects on cognition is not well understood. Here we use simultaneous fast fMRI–EEG to test how sleep deprivation modulates cognitive, neural and fluid dynamics in the human brain. We demonstrate that attentional failures during wakefulness after sleep deprivation are tightly orchestrated in a series of brain–body changes, including neuronal shifts, pupil constriction and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow pulsations, pointing to a coupled system of fluid dynamics and neuromodulatory state. CSF flow and hemodynamics are coupled to attentional function within the awake state, with CSF pulsations following attentional impairment. The timing of these dynamics is consistent with a vascular mechanism regulated by neuromodulatory state. The attentional costs of sleep deprivation may thus reflect an irrepressible need for rest periods driven by a central neuromodulatory system that regulates both neuronal and fluid physiology.