2025-11-21 ワシントン大学セントルイス校
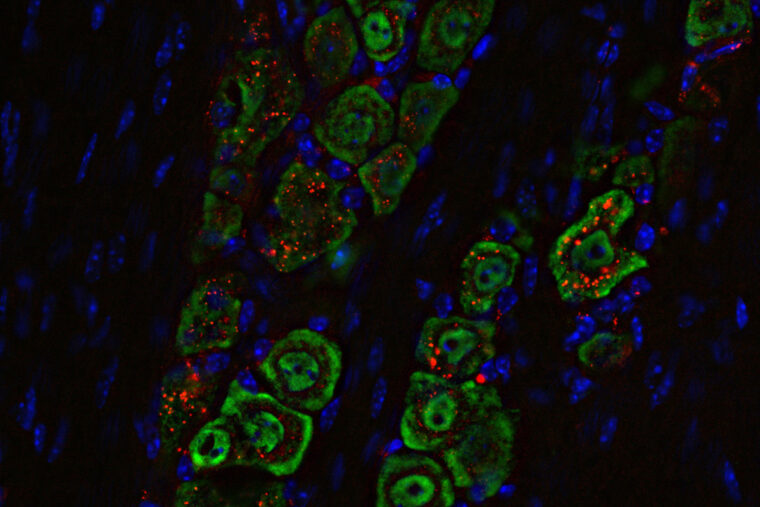
Using unsupervised machine learning, researchers in Rohit Pappu’s lab uncovered a finite number of grammars referred to as GIN clusters. The analysis showed that specific GIN clusters were associated with determining the localization preferences of proteins in cells. (Image: Pappu lab)
<関連情報>
- https://source.washu.edu/2025/11/understanding-intrinsically-disordered-protein-regions-and-their-roles-in-cancer/
- https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(25)01191-2
ヒトプロテオームにまたがる予測される本質的に無秩序な領域の分子文法 Molecular grammars of predicted intrinsically disordered regions that span the human proteome
Kiersten M. Ruff ∙ Matthew R. King ∙ Alexander W. Ying ∙ … ∙ Xiaolei Su ∙ Cigall Kadoch ∙ Rohit V. Pappu
Cell Published:November 12, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2025.10.019
Highlights
- Non-random amino acid compositions and sequence patterns define IDR molecular grammars
- NARDINI+ is an algorithm that identifies molecular grammars within individual IDRs•GIN is a resource that organizes grammars into distinct, IDRome-spanning clusters
- Distinct IDR grammars and GIN clusters are associated with spatiotemporal regulation
Summary
Intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) of proteins are defined by molecular grammars. This refers to IDR-specific non-random amino acid compositions and non-random patterning of distinct pairs of amino acid types. Here, we introduce grammars inferred using NARDINI+ (GIN) as a resource that uncovers IDR-specific and IDRome-spanning grammars. Using GIN-enabled analyses, we find that specific IDR features and GIN clusters are associated with distinct biological processes, intra-cellular localization preferences, specialized molecular functions, and functionalization as assessed by cellular fitness correlations. IDRs with exceptional grammars, defined as sequences with high-scoring non-random features, are harbored in proteins and complexes that enable spatial and temporal sorting of biochemical activities within the nucleus. Overall, GIN can be used to extract sequence-function relationships of individual IDRs or clusters of IDRs, to redesign extant IDRs or design de novo IDRs, to perform evolutionary analyses through the lens of molecular grammars and GIN clusters, and to make sense of IDR-specific disease-associated mutations.