2025-11-26 カリフォルニア大学リバーサイド校(UCR)
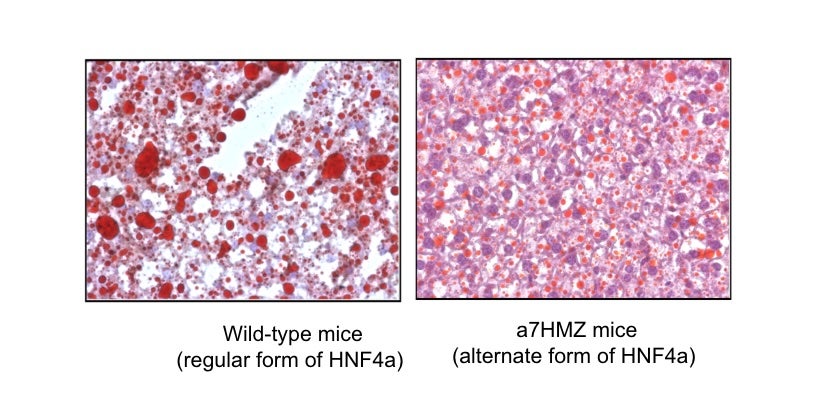
Oil red O staining of livers of mice fed diet high in soybean oil shows smaller fat droplets in the α7HMZ livers compared to those from wild-type mice. (Sonia Deol/UCR)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucr.edu/articles/2025/11/26/study-links-americas-favorite-cooking-oil-obesity
- https://www.jlr.org/article/S0022-2275(25)00195-6/fulltext
P2-HNF4αはリノール酸代謝を変化させ、大豆油誘発性肥満を軽減する:オキシリピンの役割 P2-HNF4α Alters Linoleic Acid Metabolism and Mitigates Soybean Oil-Induced Obesity: Role for Oxylipins
Poonamjot Deol ∙ Johannes Fahrmann ∙ Dmitry Grapov ∙ … ∙ Brett Phinney ∙ Bruce D. Hammock ∙ Frances M. Sladek
Journal of Lipid Research Published:October 28, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100932
ABSTRACT
Oxylipins – oxidized metabolites of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) – are associated with several pathological conditions. We previously showed that oxylipin metabolites of linoleic acid (LA) and alpha-linolenic acid positively correlate with obesity in wild-type (WT) mice fed a high fat diet (35% kcal fat) based on soybean oil (SO). Here, we compare the effect of the SO diet (10% kcal LA) to an isocaloric diet based on coconut oil (CO) that is low in LA (2% kcal) in HNF4α exon swap male mice that express only the P2 form of HNF4α (α7HMZ). α7HMZ mice gained significantly less weight on the SO diet than WT mice and exhibited neither glucose intolerance nor fatty liver as did the WT mice. Untargeted metabolomics of the liver revealed increased levels of LA and decreased levels of PUFA-derived C18 diols in α7HMZ compared to WT. Proteomics identified decreased levels of several enzymes involved in PUFA metabolism (CYP2Cs, EPHX1, FADS2, ACOX1/2) as the likely cause of decreased diols. Correlation analysis of hepatic oxylipins with body weight, coupled with a 16-week treatment with a soluble epoxide inhibitor (sEHI), identified the oxylipins most likely to be potential drivers of obesity as 9,10-DiHOME, 12,13-DiHOME, 9,10-DiHODE and 12,13-DiHODE. Finally, while neither the CO nor SO diet induced a pro-inflammatory cytokine profile in the liver, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), several tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates and glycerol-alpha-phosphate and β-hydroxybutyrate were increased in α7HMZ, suggesting a potential role for mitochondria in the resistance to diet-induced obesity.


