2025-12-08 アメリカ国立衛生研究所 (NIH)
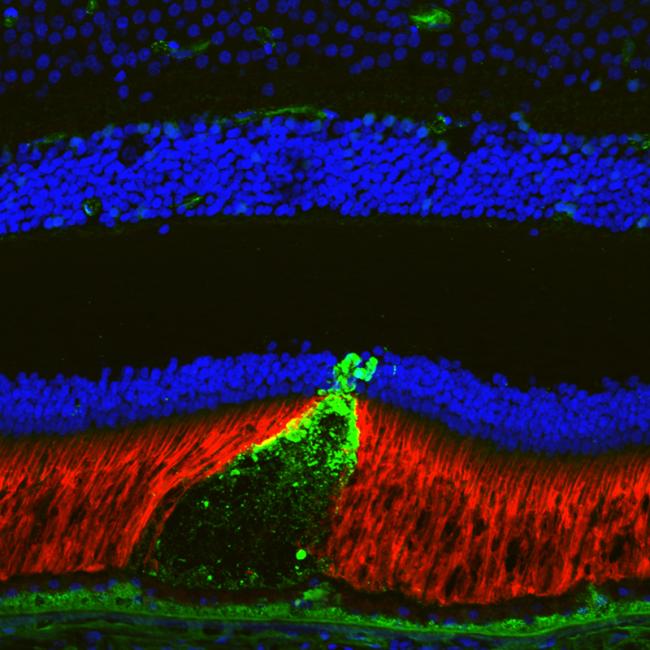
Image of a reticular pseudodrusen appears as a cone-shaped structure with its base at the retinal pigment epithelium, and it disrupts the outer retina (red).Dr. Erica Fletcher, University of Melbourne
<関連情報>
- https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/researchers-find-genetic-basis-important-risk-factor-blinding-eye-disease
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-65903-9
HTRA1 /lncRNA HTRA1-AS1は加齢黄斑変性の網状偽洞の遺伝的リスクにおいて補体関与なしで優位である HTRA1/lncRNA HTRA1-AS1 dominates in age-related macular degeneration reticular pseudodrusen genetic risk with no complement involvement
Samaneh Farashi,Carla J. Abbott,Brendan R. E. Ansell,Zhichao Wu,Lebriz Altay,Ella Arnon,Louis Arnould,Yelena Bagdasarova,Konstantinos Balaskas,Fred K. Chen,Emily Chew,Itay Chowers,Steven Clarke,Catherine Cukras,Cécile Delcourt,Marie-Noëlle Delyfer,Anneke I. den Hollander,Sascha Fauser,Robert P. Finger,Pierre-Henry Gabrielle,Jiru Han,Lauren A. B. Hodgson,Ruth Hogg,Frank G. Holz,MACUSTAR consortium,NICOLA consortium,On behalf of the Reticular Pseudodrusen Consortium,…
Nature Communications Published:08 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-65903-9
Abstract
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a multifactorial retinal disease with a large genetic risk contribution. Reticular pseudodrusen (RPD) is a sub-phenotype of AMD with a high risk of progression to late vision threatening AMD. In a genome-wide association study of 2165 AMD+/RPD+ and 4181 AMD+/RPD- compared to 7639 control participants, both chromosomes 1 (CFH) and 10 (ARMS2/HTRA1) major AMD risk loci are reidentified. However association is only detected for the chromosome 10 locus when comparing AMD+/RPD+ to AMD+/RPD- cases. The chromosome 1 locus is notably absent. The chromosome 10 RPD risk region contains a long non-coding RNA HTRA1-AS1 (ENSG00000285955/BX842242.1) which colocalizes with genetic markers of retinal thickness. HTRA1-AS1 has a strong retinal eQTL signal, pinpointing the parafoveal photoreceptor outer segment layer. Whole genome sequencing of phenotypically extreme RPD cases identifies even stronger enrichment for the chromosome 10 risk genotype.