2025-12-11 東京科学大学
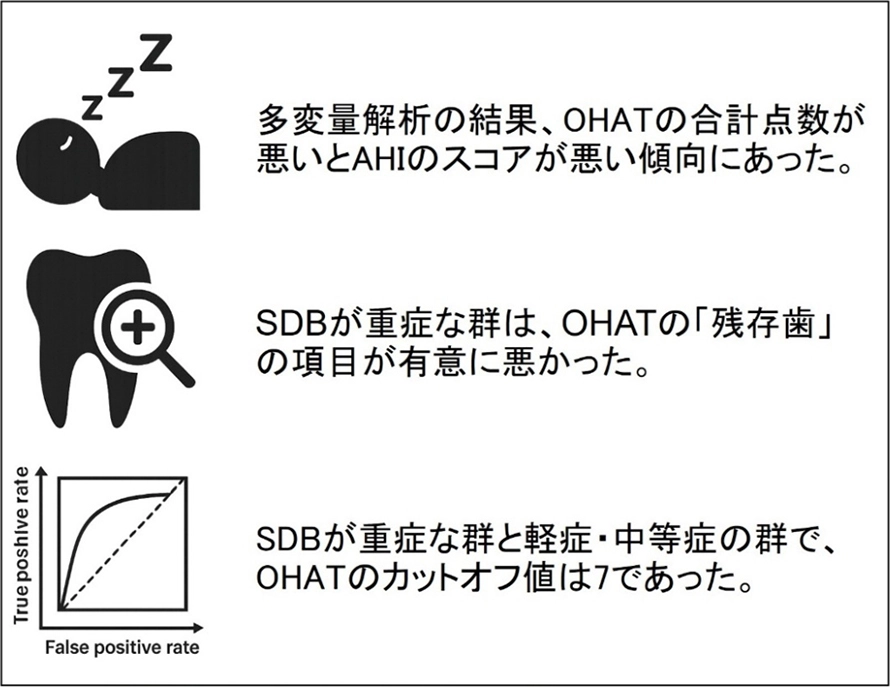
図1. 本研究で明らかになった成果
AHI:1時間当たりの無呼吸・低呼吸の回数、OHAT:口腔健康状態のスコア、SDB:睡眠関連呼吸障害
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/fiktytosj7t5
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2808&prevId=&key=6bcf06e76381892bf2aa53ad88781dc5.pdf
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/joor.70109
回復期リハビリテーション病棟における脳卒中後患者の口腔衛生状態と睡眠障害呼吸:横断研究 Oral Health Status and Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Post-Stroke Patients in Convalescent Rehabilitation Wards: A Cross-Sectional Study
Ryosuke Yanagida, Kohei Yamaguchi, Kazuharu Nakagawa, Kanako Yoshimi, Takami Hino, Ayumi Kisara, Haruka Tohara
Journal of Oral Rehabilitation Published: 24 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.70109
ABSTRACT
Background
A bidirectional relationship exists between sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) and stroke. Post-stroke patients have worse oral health status.
Objectives
Post-stroke patients with worse SDB would also have worse oral health status.
Methods
Post-stroke patients in convalescent rehabilitation wards were enrolled in this study. An overnight sleep test using WatchPAT to measure the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) was conducted. Each oral health assessment tool (OHAT) score between three groups divided by SDB severity was compared, and binary logistic regression analysis was used to assess the association between the total OHAT score and AHI. Also, a receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed using the total OHAT score for severe or non-severe SDB.
Results
Among the 196 participants enrolled, 140 participants (78 men and 62 women; mean age, 73.3 ± 12.4 years) underwent a sleep test, with 91 completing it. Significant differences were found between non- or mild SDB and severe SDB groups, as well as between moderate SDB and severe SDB groups in terms of natural teeth and total OHAT score. Binary logistic regression analysis revealed a significant association between AHI and total score of OHAT after adjusting for confounding factors. The cut-off value of the total OHAT score for severe or non-severe SDB was seven, with sensitivity and specificity of 0.524 and 0.735, respectively.
Conclusion
This study revealed that oral health status is associated with SDB severity, highlighting the need for dental professionals in convalescent rehabilitation wards to be involved with SDB.