2025-12-25 東京科学大学
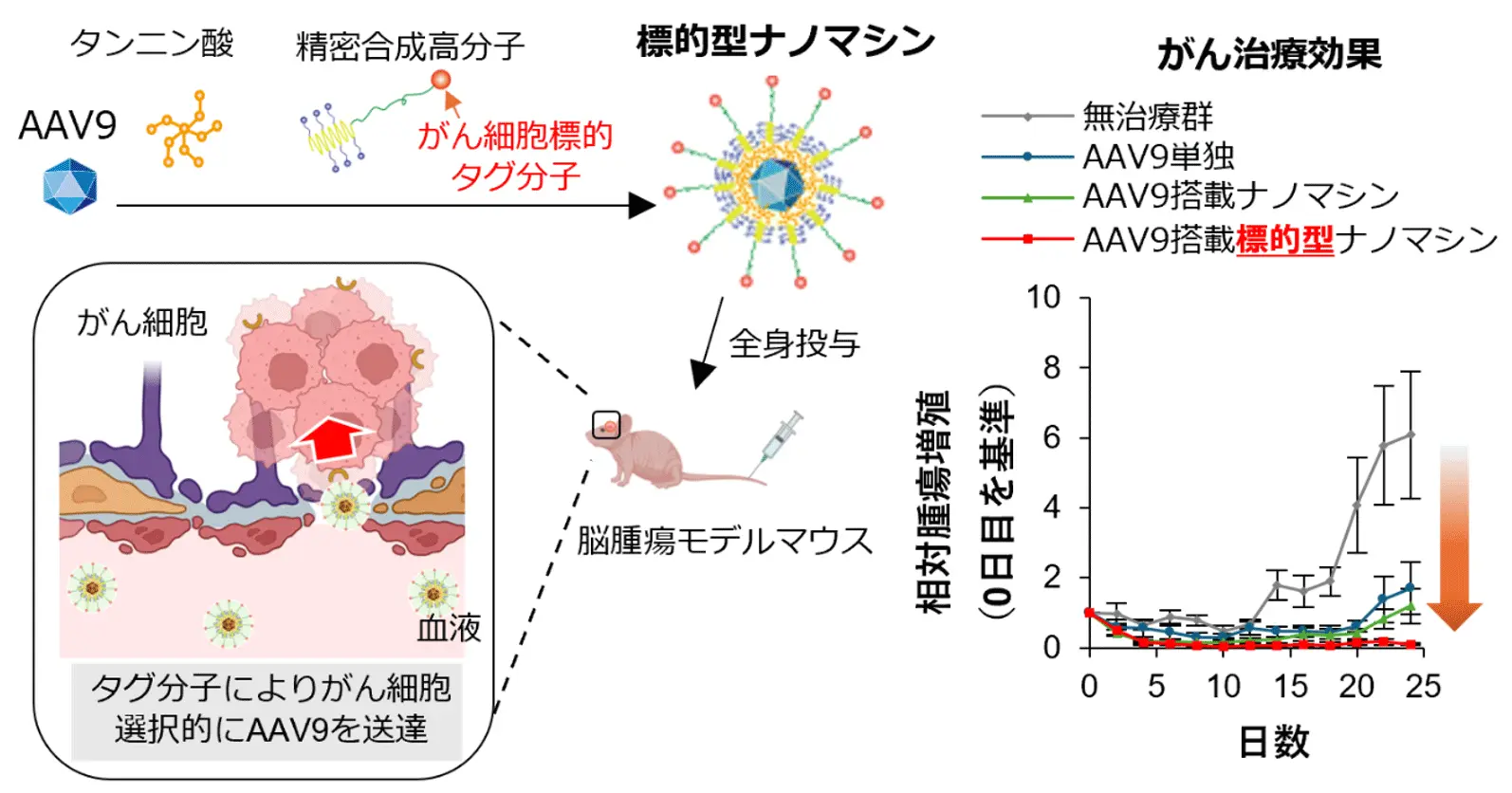
図1.タグ分子を利用した標的型ナノマシンがAAV9をがん細胞にピンポイントで送達し、効率的ながん治療を達成
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/xe3xry3s9vwt
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2957&prevId=&key=2bdad84690cb60968b54726321f70748.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365925010910
タンニン酸とフェニルボロン酸ポリマーからなる腫瘍標的アデノ随伴ウイルス搭載複合体による同所性膠芽腫治療 Tumor-targeted adeno associated virus-loaded complexes comprising tannic acid and phenylboronic acid-polymers for orthotopic glioblastoma therapy
Nozomi Matsudaira, Yuto Honda, Hiroaki Kinoh, Xueying Liu, Shuhei Nagao, Shoko Matsutomo-Nitta, Guo Haochen, Hiromi Hayashita-Kinoh, Miho Aizawa, Kyohei Muguruma, Yutaka Miura, Atushi Shishido, Takashi Okada, Nobuhiro Nishiyama
Journal of Controlled Release Available online: 28 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.114477
Highlights
- A tumor-targeted AAV-loaded complex was prepared via sequential assembly.
- The tumor-targeted complex showed high transduction efficiency in glioblastoma.
- Polymer coating reduces neutralization by pre-existing antibodies.
- The tumor-targeted complex treats orthotopic glioblastoma without hepatotoxicity.
Abstract
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors have emerged as one of the most promising viral vectors for gene therapy due to their capacity for long-term transgene expression, strong safety profile and low pathogenicity, and have been applied to the treatment of refractory cancer such as glioblastoma (GBM). However, AAV-mediated cancer gene therapy faces significant obstacles, including poor tumor targeting and neutralization by pre-existing antibodies (Abs). In this study, we developed a novel GBM-targeted AAV delivery platform, the cyclic RGD-functionalized ternary complex (cRGD-ternary complex). This complex is constructed through the self-assembly of AAV, tannic acid, and cRGD-conjugated phenylboronic acid polymers. cRGD serves as a ligand targeting αvβ3/αvβ5 integrins, which are highly expressed on GBM cells. In vitro, the cRGD-ternary complex effectively evaded neutralizing Abs due to its polymer shell and maintained high gene transduction efficiency. In an orthotopic GBM mouse model, systemic administration of cRGD-ternary complex significantly enhanced gene transduction in tumors and achieved substantial tumor suppression over 24 days. Furthermore, the cRGD-ternary complex showed therapeutic efficacy comparable to AAV alone at three-fold higher dose, with negligible hepatotoxicity. This platform successfully integrates active tumor targeting, immune evasion, and efficient gene transduction, overcoming critical limitations of AAV and showing significant potential for GBM gene therapy.