2026-01-21 産業技術総合研究所
<関連情報>
- https://www.aist.go.jp/aist_j/press_release/pr2026/pr20260121_2/pr20260121_2.html
- https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/54/2/gkaf1502/8426369
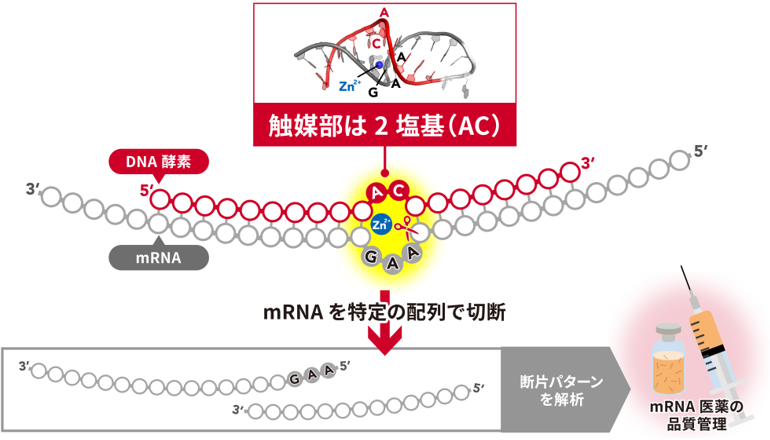
最小限のRNA切断DNAザイムとその触媒機構 A minimal RNA-cleaving DNAzyme and its catalytic mechanism
Kazuhiko Yamasaki,Rika Inomata,Tomoko Yamasaki,Tomomi Kubota,Naoyuki Miyashita,Koh Takeuchi,Makoto Miyagishi
Nucleic Acids Research Published:15 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf1502
Abstract
Although natural sources of enzymes are limited to protein and RNA, some artificial DNAs exhibit catalytic activities. Representative functions of such DNAs, i.e. DNAzymes, are cleavage and ligation of nucleic acids. Here we developed a minimal DNAzyme with an RNA-cleaving activity by in vitro selection and secondary structure-based design. Its catalytic and substrate cores are only two and three nucleotides, respectively. This DNAzyme showed strict Zn2+ dependence at optimal pH 7.0–7.5. To elucidate its catalytic mechanism, we determined its three-dimensional structure by X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The results consistently showed a B-DNA-like structure with base pairing and stacking throughout the molecule, unlike the kinked structures of larger DNAzymes. Notably, an A-base in the catalytic loop and a G-base in the substrate loop formed a non-Watson–Crick base pair. The catalytic Zn2+ coordinates to N7 of that G-base, enabling the Zn2+-hydrated water molecules to contacts O2′ and O5′ at the cleavage site. Considering that Zn(OH)+ and Zn2+ co-exist at the enzyme’s optimal pH, we propose a catalytic mechanism whereby these ions act as the base withdrawing H+ from O2′ and the acid donating H+ to O5′, generating the cleaved ends with 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate and OH groups.