2026-01-30 ワシントン州立大学(WSU)
<関連情報>
- https://news.wsu.edu/press-release/2026/01/30/study-identifies-alternate-path-for-inflammation-that-could-improve-ra-treatment/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41423-026-01386-y
TWEAK受容体(Fn14)は、関節リウマチ滑膜線維芽細胞におけるTNF-α誘発炎症を増悪させ、抗TNF-α療法への反応に影響を与える TWEAK receptor (Fn14) exacerbates TNF-α-induced inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and influences response to anti-TNF-α therapy
Farheen S. Shaikh,Meena A. Shanta,Anil K. Singh,Alexis M. Daniels,Sadik A. Khuder,Geoffrey M. Thiele,George W. Reed,Joel M. Kremer,Dimitrios A. Pappas,Jeffrey R. Curtis,James R. O’Dell,Madhu M. Ouseph,David A. Fox & Salahuddin Ahmed
Cellular & Molecular Immunology Published:30 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-026-01386-y
Abstract
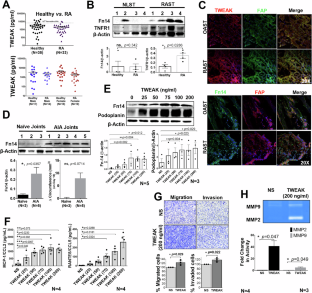
The use of TNF inhibitors (TNFis) has revolutionized the management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other autoimmune conditions, but some patients remain resistant to TNFis, for which the molecular mechanisms remain elusive. Our study reveals novel molecular crosstalk between TWEAK/Fn14 and TNF-α signaling and its potential implications for therapy resistance. Elevated Fn14 expression was observed in human synovial tissues and joint homogenates from adjuvant-induced arthritis rats. Low doses of TNF-α and TWEAK synergistically induced inflammation in human RA synovial fibroblasts (RASFs). Furthermore, increased expression of the TWEAK receptor (Fn14) was sufficient for TNF-α to synergistically induce RANTES/CCL5 and MMP-1. In contrast, Fn14 knockdown suppressed the expression of TNF-α-induced adhesion molecules (PDPN, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and cadherin-11) and inflammatory chemokines (MCP-1/CCL2, RANTES/CCL5, IL-8/CXCL8, and ITAC/CXCL11). Blocking Fn14 with an antagonist (L524-0366) suppressed TNF-α-induced phosphorylation of the kinases JNK, p38, and PKCδ and consequently decreased MCP-1/CCL2, RANTES/CCL5, ITAC/CXCL11, and MMP-1 production. RNA-sequencing analysis revealed >200 differentially expressed genes significantly affected by Fn14 knockdown in TNF-α-activated RASFs. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) revealed significant enrichment of IFN-α and IFN-γ pathway responses in the NC siRNA/TNF-α group compared with the Fn14 siRNA/TNF-α group. Administration of L524-0366 (10 mg/kg) intraperitoneally daily from the onset of disease ameliorated collagen antibody-induced arthritis in mice. These findings reveal that TNF-α utilizes the TWEAK/Fn14 axis to induce inflammation, suggesting the potential benefits of targeting TWEAK/Fn14 as an adjunct therapy with TNF inhibitors.