2022-03-16 南洋(ナンヤン)理工大学(NTU)
・この液滴は分子の「トロイの木馬」のような働きをし、細胞を騙して中に入れさせ、いったん中に入ると液滴は溶けて、病気を治療するための薬剤を運ぶ生体高分子を放出します。・イカのくちばしから抽出したペプチドを合成して、この微小液滴を形成した。そして、液液相分離(LLPS)と呼ばれるプロセスによって、生体高分子をその内部に封じ込めることができた。
・微小液滴は液体のような性質を持つようになり、ヒトの細胞に融合して薬剤を沈着させることができるようになった。
・遺伝子治療、がん治療、ワクチンデリバリーに、より速く、より安全で、より効果的で、mRNAベースのワクチンも含めてより適したものになることが期待されます。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ntu.edu.sg/docs/default-source/corporate-ntu/hub-news/ntu-singapore-scientists-develop-novel-trojan-horse-drug-delivery-system-using-protein-based-microdroplets.pdf?sfvrsn=d6fa5b46_1
- https://www.ntu.edu.sg/news/detail/sneaking-large-drug-carrying-biological-molecules-into-human-cells
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-021-00854-4
高分子治療薬の細胞質への直接導入および酸化還元活性化放出のための相分離性ペプチド Phase-separating peptides for direct cytosolic delivery and redox-activated release of macromolecular therapeutics
Yue Sun , Sze Yi Lau , Zhi Wei Lim , Shi Chieh Chang , Farid Ghadessy , Anthony Partridge and Ali Miserez
nature chemistry, 14, pages274–283 (2022)
Abstract
Biomacromolecules are highly promising therapeutic modalities to treat various diseases. However, they suffer from poor cellular membrane permeability, limiting their access to intracellular targets. Strategies to overcome this challenge often employ nanoscale carriers that can get trapped in endosomal compartments. Here we report conjugated peptides that form pH- and redox-responsive coacervate microdroplets by liquid–liquid phase separation that readily cross the cell membrane. A wide range of macromolecules can be quickly recruited within the microdroplets, including small peptides, enzymes as large as 430 kDa and messenger RNAs (mRNAs). The therapeutic-loaded coacervates bypass classical endocytic pathways to enter the cytosol, where they undergo glutathione-mediated release of payload, the bioactivity of which is retained in the cell, while mRNAs exhibit a high transfection efficiency. These peptide coacervates represent a promising platform for the intracellular delivery of a large palette of macromolecular therapeutics that have potential for treating various pathologies (for example, cancers and metabolic diseases) or as carriers for mRNA-based vaccines.
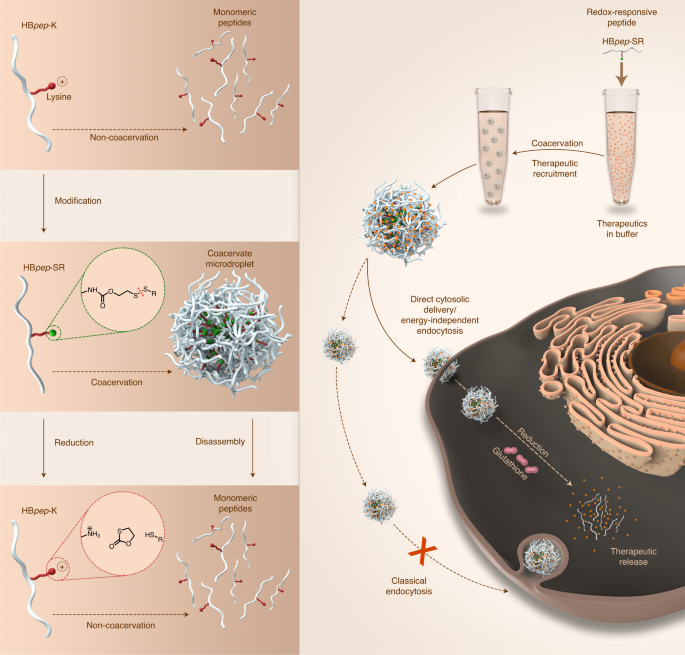
Fig. 1: Design of redox-responsive peptide coacervates HBpep-SR with direct cytosolic entry that bypasses classical endocytosis.