2023-06-05 ミシガン大学
◆モデルは機械学習を使用し、タンパク質とナノ粒子の相互作用を予測する。このモデルは、タンパク質とナノ粒子の相互作用を予測するための最も優れたモデルである。研究チームはさらに、バイオフィルムやウイルスなど、他の生物フィルムや微生物の研究を進める予定である。
<関連情報>
- https://news.umich.edu/nanobiotics-ai-for-discovering-where-and-how-nanoparticles-bind-with-proteins/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s43588-023-00438-x
タンパク質とナノ粒子におけるナノスケール相互作用のドメイン診断的予測 Domain-agnostic predictions of nanoscale interactions in proteins and nanoparticles
Jacob Charles Saldinger,Matt Raymond,Paolo Elvati & Angela Violi
Nature Computational Science Published:01 May 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43588-023-00438-x
Abstract
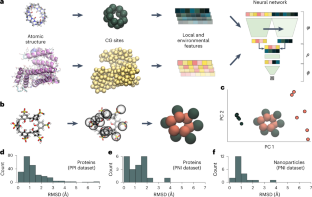
Although challenging, the accurate and rapid prediction of nanoscale interactions has broad applications for numerous biological processes and material properties. While several models have been developed to predict the interaction of specific biological components, they use system-specific information that hinders their application to more general materials. Here we present NeCLAS, a general and efficient machine learning pipeline that predicts the location of nanoscale interactions, providing human-intelligible predictions. NeCLAS outperforms current nanoscale prediction models for generic nanoparticles up to 10–20 nm, reproducing interactions for biological and non-biological systems. Two aspects contribute to these results: a low-dimensional representation of nanoparticles and molecules (to reduce the effect of data uncertainty), and environmental features (to encode the physicochemical neighborhood at multiple scales). This framework has several applications, from basic research to rapid prototyping and design in nanobiotechnology.