2023-09-06 インペリアル・カレッジ・ロンドン(ICL)
◆これは初めての研究であり、乳がん細胞に変化する際に何が起こるのかについて重要な手がかりを提供し、特に後で初めて子供を持つ女性が初産の年齢よりも長期間にわたり乳がんリスクが高いように見える理由を説明する可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://www.imperial.ac.uk/news/247414/research-sheds-light-breast-cancer-might/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-40608-z
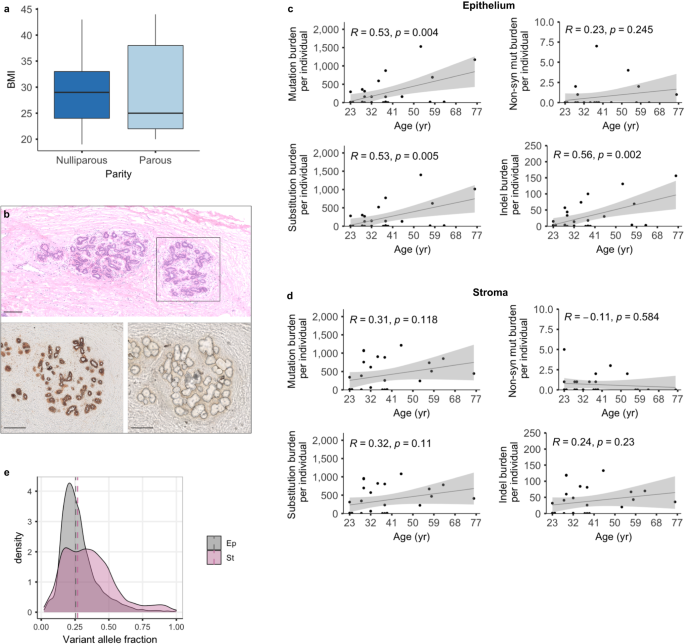
成人の健康な経産婦と経産婦の乳房の突然変異の状況 The mutational landscape of the adult healthy parous and nulliparous human breast
Biancastella Cereser,Angela Yiu,Neha Tabassum,Lisa Del Bel Belluz,Sladjana Zagorac,Kenneth Russell Zapanta Ancheta,Rongrong Zhong,Cristian Miere,Alicia Rose Jeffries-Jones,Nina Moderau,Benjamin Werner & Justin Stebbing
Nature Communications Published:06 September 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40608-z
Abstract
The accumulation of somatic mutations in healthy human tissues has been extensively characterized, but the mutational landscape of the healthy breast is still poorly understood. Our analysis of whole-genome sequencing shows that in line with other healthy organs, the healthy breast during the reproduction years accumulates mutations with age, with the rate of accumulation in the epithelium of 15.24 ± 5 mutations/year. Both epithelial and stromal compartments contain mutations in breast-specific driver genes, indicative of subsequent positive selection. Parity- and age-associated differences are evident in the mammary epithelium, partly explaining the observed difference in breast cancer risk amongst women of different childbearing age. Parity is associated with an age-dependent increase in the clone size of mutated epithelial cells, suggesting that older first-time mothers have a higher probability of accumulating oncogenic events in the epithelium compared to younger mothers or nulliparous women. In conclusion, we describe the reference genome of the healthy female human breast during reproductive years and provide evidence of how parity affects the genomic landscape of the mammary gland.