2024-03-19 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/ptsd-in-pregnant-women-may-affect-the-risk-of-adhd-in-the-child
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/european-psychiatry/article/prenatal-maternal-ptsd-as-a-risk-factor-for-offspring-adhd-a-registerbased-swedish-cohort-study-of-553-766-children-and-their-mothers/1DC1C7EDB59B11111E9998023B138561
出生前の母親のPTSDは、子供のADHDの危険因子である: 553 766人の子どもとその母親の登録ベースのスウェーデンのコホート研究 Prenatal maternal PTSD as a risk factor for offspring ADHD: A register-based Swedish cohort study of 553 766 children and their mothers
Michael Borgert,Amandah Melin,Anna-Clara Hollander and Syed Rahman
European Psychiatry Published:01 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1192/j.eurpsy.2024.21
Abstract
Background
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is highly heritable, though environmental factors also play a role. Prenatal maternal stress is suggested to be one such factor, including exposure to highly distressing events that could lead to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The aim of this study is to investigate whether prenatal maternal PTSD is associated with offspring ADHD.
Method
A register-based retrospective cohort study linking 553 766 children born in Sweden during 2006–2010 with their biological parents. Exposure: Prenatal PTSD. Outcome: Offspring ADHD. Logistic regression determined odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for ADHD in the offspring. Adjustments were made for potential covariates, including single parenthood and possible indicators of heredity measured as parental ADHD and maternal mental disorders other than PTSD. Subpopulations, excluding children with indicators of heredity, were investigated separately.
Results
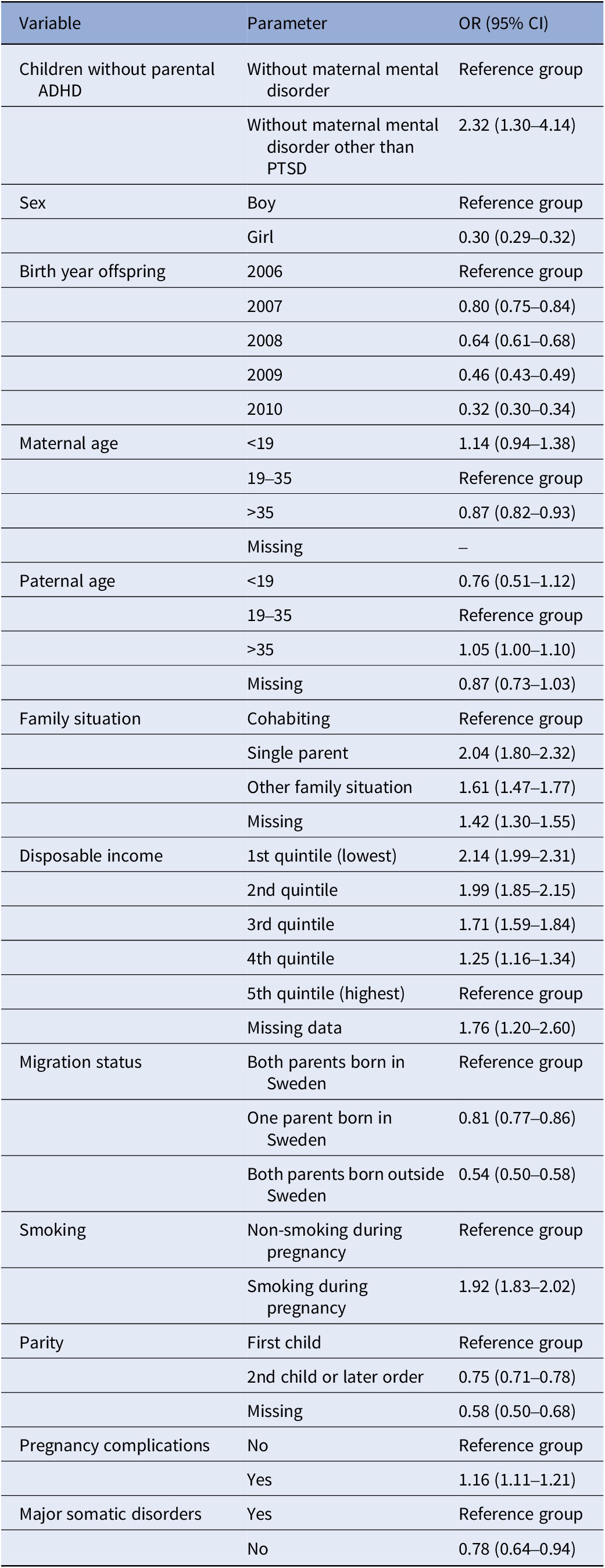
In the crude results, including all children, prenatal PTSD was associated with offspring ADHD (OR: 1.79, 95% CI: 1.37–2.34). In children with indicators of heredity, the likelihood was partly explained by it. Among children without indicators of heredity, PTSD was associated with offspring ADHD (OR: 2.32, 95% CI: 1.30–4.14), adjusted for confounders.
Conclusions
Prenatal maternal PTSD is associated with offspring ADHD regardless of indicators of heredity, such as parental ADHD or maternal mental disorder other than PTSD. The association is partly explained by heredity and socioeconomic factors. If replicated in other populations, preferably using a sibling design, maternal PTSD could be identified as a risk factor for ADHD.