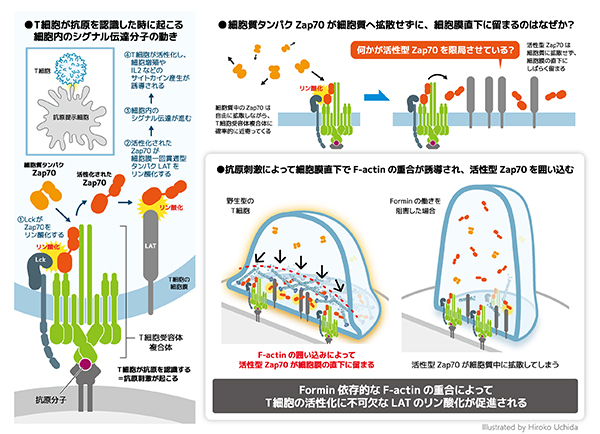
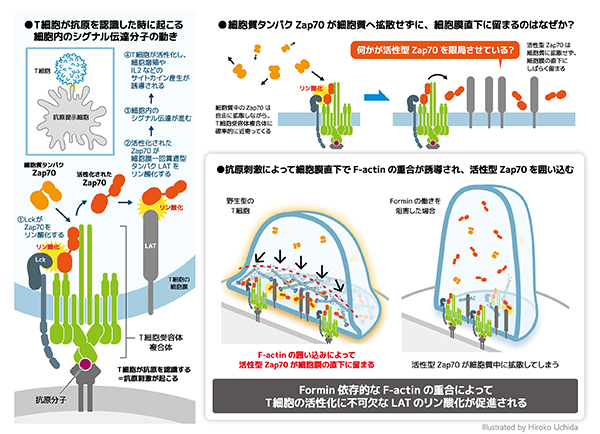
2024-02-07 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/ai-model-as-diabetes-early-warning-system-when-driving.html
- https://ai.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/AIoa2300013
生体信号から健康状態を推測する機械学習 – 実車運転中の糖尿病患者の低血糖を検出 Machine Learning to Infer a Health State Using Biomedical Signals — Detection of Hypoglycemia in People with Diabetes while Driving Real Cars
Vera Lehmann, M.D., Ph.D. , Thomas Zueger, M.D. , Martin Maritsch, Ph.D. , Michael Notter , Simon Schallmoser, M.Sc. , Caterina Bérubé, Ph.D. , Caroline Albrecht, M.D. , +7, and Christoph Stettler, M.D.
New England Journal of Medicine AI Published January 31, 2024
DOI: 10.1056/AIoa2300013
Abstract
BACKGROUND
Hypoglycemia, one of the most dangerous acute complications of diabetes, poses a substantial risk for vehicle accidents. To date, both reliable detection and warning of hypoglycemia while driving remain unmet needs, as current sensing approaches are restricted by diagnostic delay, invasiveness, low availability, and high costs. This research aimed to develop and evaluate a machine learning (ML) approach for the detection of hypoglycemia during driving through data collected on driving characteristics and gaze/head motion.
METHODS
We collected driving and gaze/head motion data (47,998 observations) during controlled euglycemia and hypoglycemia from 30 individuals with type 1 diabetes (24 male participants; mean ±SD age, 40.1±10.3 years; mean glycated hemoglobin value, 6.9±0.7% [51.9±8.0 mmol/mol]) while participants drove a real car. ML models were built and evaluated to detect hypoglycemia solely on the basis of data regarding driving characteristics and gaze/head motion.
RESULTS
The ML approach detected hypoglycemia with high accuracy (area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve [AUROC], 0.80±0.11). When restricted to either driving characteristics or gaze/head motion data only, the detection performance remained high (AUROC, 0.73±0.07 and 0.70±0.16, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS
Hypoglycemia could be detected noninvasively during real car driving with an ML approach that used only data on driving characteristics and gaze/head motion, thus improving driving safety and self-management for people with diabetes. Interpretable ML also provided novel insights into behavioral changes in people driving while hypoglycemic. (Funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation and others; ClinicalTrials.gov numbers, NCT04569630 and NCT05308095.)