2024-07-25 ノースカロライナ州立大学(NCState)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ncsu.edu/2024/07/array-pinpoints-imprinted-genes-with-potential-links-to-disease/
- https://epicom.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s43682-024-00028-6
ヒトインプリンクトームに対する初のインフィニウムDNAメチル化アレイの作成と検証 Creation and validation of the first infinium DNA methylation array for the human imprintome
Natalia Carreras-Gallo,Varun B. Dwaraka,Dereje D. Jima,David A. Skaar,Tavis L. Mendez,Antonio Planchart,Wanding Zhou,Randy L. Jirtle,Ryan Smith & Cathrine Hoyo
Epigenetics Communications Published:10 July 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s43682-024-00028-6
Abstract
Background
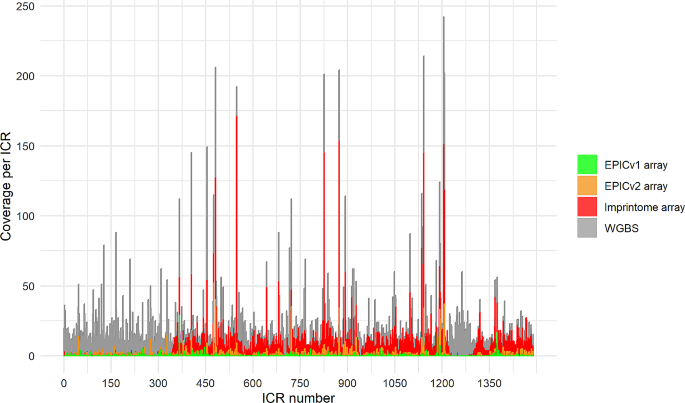
Differentially methylated imprint control regions (ICRs) regulate the monoallelic expression of imprinted genes. Their epigenetic dysregulation by environmental exposures throughout life results in the formation of common chronic diseases. Unfortunately, existing Infinium methylation arrays lack the ability to profile these regions adequately. Whole genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS) is the unique method able to profile the ICRs. However, it is very expensive and it requires not only a high coverage, but it is also computationally intensive to assess these regions.
Findings
To address this deficiency, we developed a custom methylation array containing 22,819 probes. Among them, 10,438 are CG probes targeting unique CpG sites, with 9,757 probes successfully mapping to 1,088 out of the 1,488 candidate ICRs recently described. To assess the performance of the array, we created matched samples processed with the Human Imprintome array and WGBS, which is the current standard method for assessing the methylation of the Human Imprintome. We compared the methylation levels from the shared CpG sites, and obtained a mean R2 = 0.569. We also created matched samples processed with the Human Imprintome array and the Infinium Methylation EPIC v2 array, and obtained a mean R2 = 0.796. Furthermore, replication experiments demonstrated high reliability (ICC: 0.799–0.945).
Conclusions
Our custom array will be useful for replicable and accurate assessment, mechanistic insight, and targeted investigation of ICRs. This tool should accelerate the discovery of ICRs associated with a wide range of diseases and exposures, and advance our understanding of genomic imprinting and its relevance in development and disease formation throughout the life course.


