2024-11-05 カリフォルニア大学リバーサイド校(UCR)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucr.edu/articles/2024/11/05/how-gophers-brought-mount-st-helens-back-life-one-day
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/microbiomes/articles/10.3389/frmbi.2024.1399416/full
セントヘレンズ山の回復した森林における微生物群集構造
Microbial community structure in recovering forests of Mount St. Helens
Mia Rose Maltz,Michael F. Allen,Michala L. Phillips,Rebecca R. Hernandez,Hannah B. Shulman,Linton Freund,Lela V. Andrews,Jon K. Botthoff,Emma L. Aronson
Frontiers in Microbiomes Published:04 November 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3389/frmbi.2024.1399416
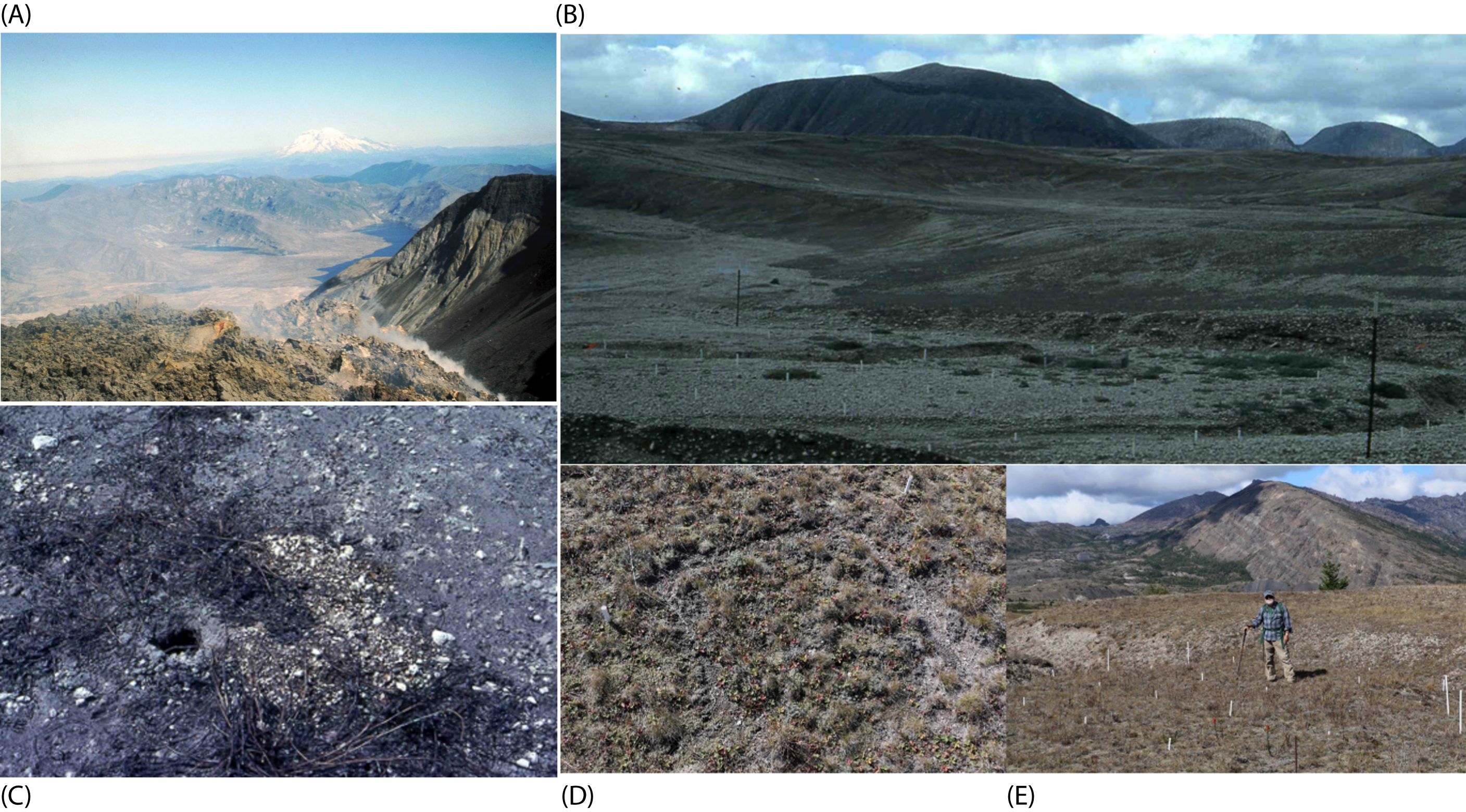
Introduction: The 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens had devastating effects above and belowground in forested montane ecosystems, including the burial and destruction of soil microbes. Soil microbial propagules and legacies in recovering ecosystems are important for determining post-disturbance successional trajectories. Soil microorganisms regulate nutrient cycling, interact with many other organisms, and therefore may support successional pathways and complementary ecosystem functions, even in harsh conditions. Historic forest management methods, such as old-growth and clearcut regimes, and locations of small mammal enclo and clearcut forests, as well as in locations of historic short-term gopher enclosures (Thomomys talpoides), to evaluate community response to forest management practices and to examine vectors for dispersing microbial consortia to the surface of the volcanic landscape. These biotic interactions may have primed ecological succession in the volcanic landscape, specifically Bear Meadow and the Pumice Plain, by creating microsite conditions conducive to primary succession and plant establishment.
Methods and results: Using molecular techniques, we examined bacterial, fungal, and AMF communities to determine how these variables affected microbial communities and soil properties. We found that bacterial/archaeal 16S, fungal ITS2, and AMF SSU community composition varied among forestry practices and across sites with long-term lupine plots and gopher enclosures. The findings also related to detected differences in C and N concentrations and ratios in soil from our study sites. Fungal communities from previously clearcut locations were less diverse than in gopher plots within the Pumice Plain. Yet, clearcut meadows harbored fewer ancestral AM fungal taxa than were found within the old-growth forest.
Discussion: By investigating both forestry practices and mammals in microbial dispersal, we evaluated how these interactions may have promoted revegetation and ecological succession within the Pumice Plains of Mount St. Helens. In addition to providing evidence about how dispersal vectors and forest structure influence post-eruption soil microbiomes, this project also informs research and management communities about belowground processes and microbial functional traits in facilitating succession and ecosystem function.