2024-11-07 アリゾナ大学
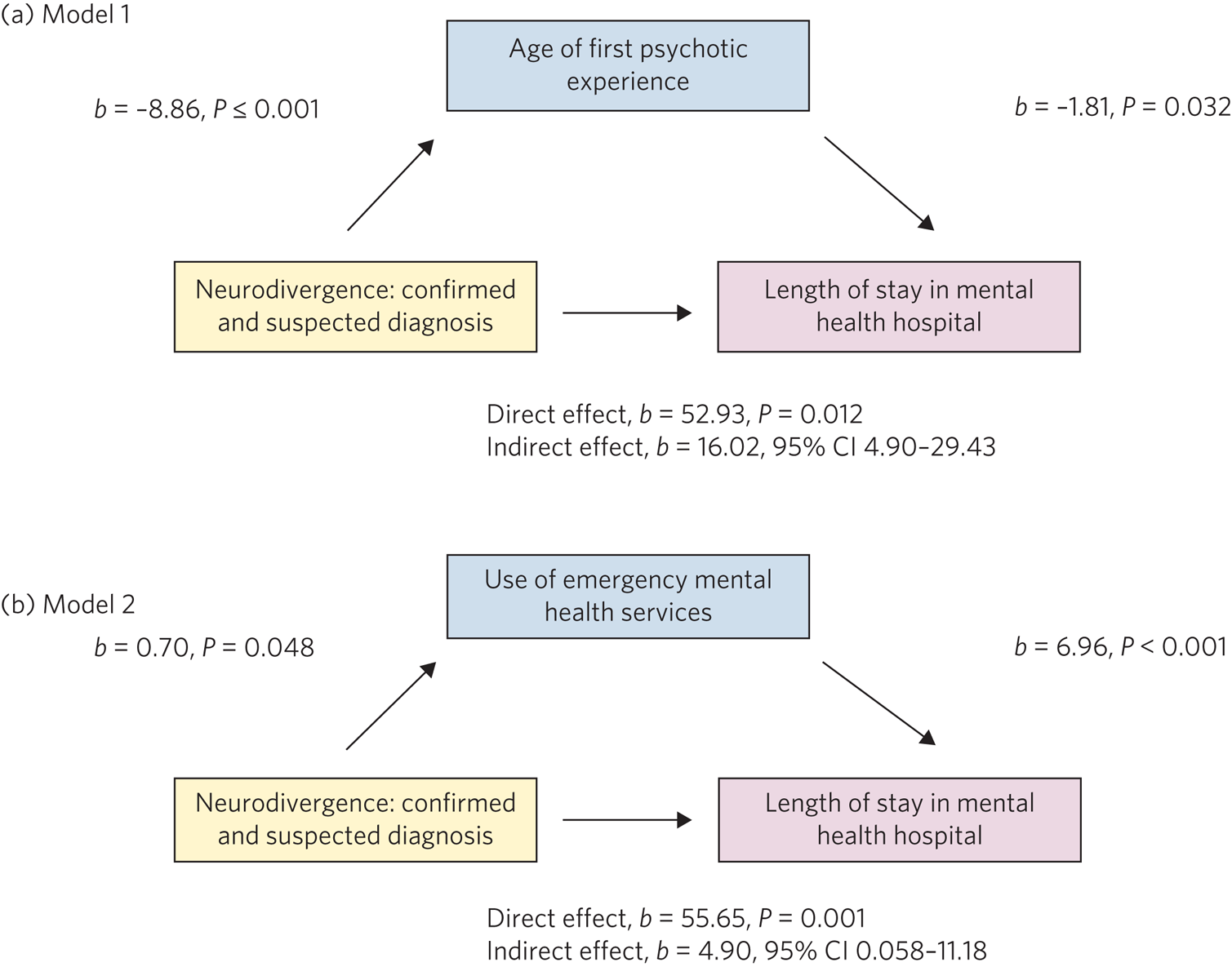
 The nonvenomous Arizona mountain kingsnake, which resembles a venomous coral snake, has a survival advantage by warning off would-be predators that avoid colorful coral snakes.
The nonvenomous Arizona mountain kingsnake, which resembles a venomous coral snake, has a survival advantage by warning off would-be predators that avoid colorful coral snakes.
John J. Wiens/Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
<関連情報>
- https://news.arizona.edu/news/new-study-maps-dramatic-100-million-year-explosion-color-signals-used-animals
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/brv.13141
生命はいかにしてカラフルになったか:色覚、アポセマティズム、性淘汰、花、果実 How life became colourful: colour vision, aposematism, sexual selection, flowers, and fruits
John J. Wiens, Zachary Emberts
Biological Reviews Published: 16 September 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.13141
ABSTRACT
Plants and animals are often adorned with potentially conspicuous colours (e.g. red, yellow, orange, blue, purple). These include the dazzling colours of fruits and flowers, the brilliant warning colours of frogs, snakes, and invertebrates, and the spectacular sexually selected colours of insects, fish, birds, and lizards. Such signals are often thought to utilize pre-existing sensitivities in the receiver’s visual systems. This raises the question: what was the initial function of conspicuous colouration and colour vision? Here, we review the origins of colour vision, fruit, flowers, and aposematic and sexually selected colouration. We find that aposematic colouration is widely distributed across animals but relatively young, evolving only in the last ~150 million years (Myr). Sexually selected colouration in animals appears confined to arthropods and chordates, and is also relatively young (generally <100 Myr). Colourful flowers likely evolved ~200 million years ago (Mya), whereas colourful fruits/seeds likely evolved ~300 Mya. Colour vision (sensu lato) appears to be substantially older, and likely originated ~400–500 Mya in both arthropods and chordates. Thus, colour vision may have evolved long before extant lineages with fruit, flowers, aposematism, and sexual colour signals. We also find that there appears to have been an explosion of colour within the last ~100 Myr, including >200 origins of aposematic colouration across nine animal phyla and >100 origins of sexually selected colouration among arthropods and chordates.