2024-11-13 ジョージア工科大学
<関連情報>
- https://research.gatech.edu/no-matter-task-new-exoskeleton-ai-controller-can-handle-it
- https://coe.gatech.edu/news/2024/11/no-matter-task-new-exoskeleton-ai-controller-can-handle-it
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-08157-7
生物学的関節モーメント推定による作業内容にとらわれない外骨格制御 Task-agnostic exoskeleton control via biological joint moment estimation
Dean D. Molinaro,Keaton L. Scherpereel,Ethan B. Schonhaut,Georgios Evangelopoulos,Max K. Shepherd & Aaron J. Young
Nature Published:13 November 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-08157-7
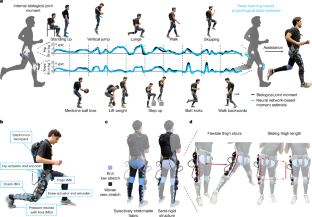
Abstract
Lower-limb exoskeletons have the potential to transform the way we move1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14, but current state-of-the-art controllers cannot accommodate the rich set of possible human behaviours that range from cyclic and predictable to transitory and unstructured. We introduce a task-agnostic controller that assists the user on the basis of instantaneous estimates of lower-limb biological joint moments from a deep neural network. By estimating both hip and knee moments in-the-loop, our approach provided multi-joint, coordinated assistance through our autonomous, clothing-integrated exoskeleton. When deployed during 28 activities, spanning cyclic locomotion to unstructured tasks (for example, passive meandering and high-speed lateral cutting), the network accurately estimated hip and knee moments with an average R2 of 0.83 relative to ground truth. Further, our approach significantly outperformed a best-case task classifier-based method constructed from splines and impedance parameters. When tested on ten activities (including level walking, running, lifting a 25 lb (roughly 11 kg) weight and lunging), our controller significantly reduced user energetics (metabolic cost or lower-limb biological joint work depending on the task) relative to the zero torque condition, ranging from 5.3 to 19.7%, without any manual controller modifications among activities. Thus, this task-agnostic controller can enable exoskeletons to aid users across a broad spectrum of human activities, a necessity for real-world viability.