2025-01-30 インペリアル・カレッジ・ロンドン (ICL)
<関連情報>
- https://www.imperial.ac.uk/news/260553/covid-19-linked-increase-biomarkers-abnormal-brain/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03426-4
SARS-CoV-2感染後のβ-アミロイド病理学的増加を示す血漿プロテオミクスの証拠 Plasma proteomic evidence for increased β-amyloid pathology after SARS-CoV-2 infection
Eugene P. Duff,Henrik Zetterberg,Amanda Heslegrave,Abbas Dehghan,Paul Elliott,Naomi Allen,Heiko Runz,Rhiannon Laban,Elena Veleva,Christopher D. Whelan,Benjamin B. Sun & Paul M. Matthews
Nature Medicine Published:30 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03426-4
Abstract
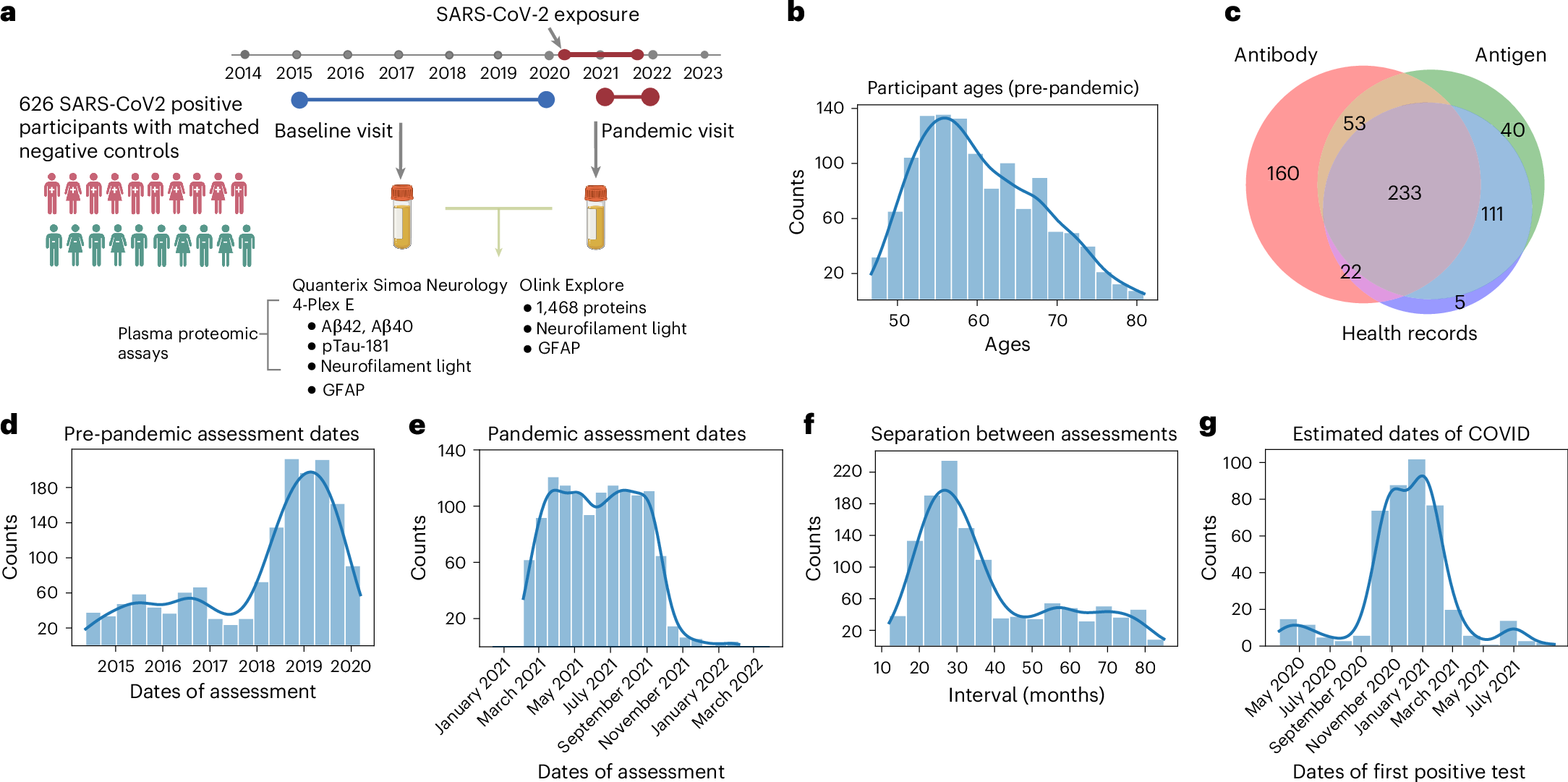
Previous studies have suggested that systemic viral infections may increase risks of dementia. Whether this holds true for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus infections is unknown. Determining this is important for anticipating the potential future incidence of dementia. To begin to do this, we measured plasma biomarkers linked to Alzheimer’s disease pathology in the UK Biobank before and after serology-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infections. SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with biomarkers associated with β-amyloid pathology: reduced plasma Aβ42:Aβ40 ratio and, in more vulnerable participants, lower plasma Aβ42 and higher plasma pTau-181. The plasma biomarker changes were greater in participants who had been hospitalized with COVID-19 or had reported hypertension previously. We showed that the changes in biomarkers were linked to brain structural imaging patterns associated with Alzheimer’s disease, lower cognitive test scores and poorer overall health evaluations. Our data from this post hoc case–control matched study thus provide observational biomarker evidence that SARS-CoV-2 infection can be associated with greater brain β-amyloid pathology in older adults. While these results do not establish causality, they suggest that SARS-CoV-2 (and possibly other systemic inflammatory diseases) may increase the risk of future Alzheimer’s disease.