2025-03-13 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202503/t20250312_903727.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08668-x
空間免疫スコアリングシステムは肝細胞癌の再発を予測する Spatial immune scoring system predicts hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence
Gengjie Jia,Peiqi He,Tianli Dai,Denise Goh,Jiabei Wang,Mengyuan Sun,Felicia Wee,Fuling Li,Jeffrey Chun Tatt Lim,Shuxia Hao,Yao Liu,Tony Kiat Hon Lim,Nye-Thane Ngo,Qingping Tao,Wei Wang,Ahitsham Umar,Björn Nashan,Yongchang Zhang,Chen Ding,Joe Yeong,Lianxin Liu & Cheng Sun
Nature Published:12 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-08668-x
Abstract
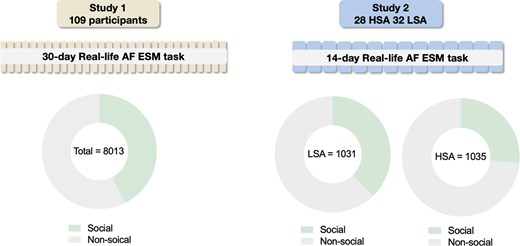
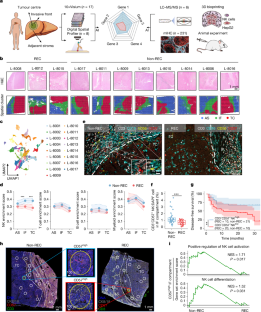
Given the high recurrence rates of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) post-resection, improved early identification of patients at high risk for post-resection recurrence would help to improve patient outcomes and prioritize healthcare resources. Here we observed a spatial and HCC recurrence-associated distribution of natural killer (NK) cells in the invasive front and tumour centre from 61 patients. Using extreme gradient boosting and inverse-variance weighting, we developed the tumour immune microenvironment spatial (TIMES) score based on the spatial expression patterns of five biomarkers (SPON2, ZFP36L2, ZFP36, VIM and HLA-DRB1) to predict HCC recurrence risk. The TIMES score (hazard ratio = 88.2, P < 0.001) outperformed current standard tools for patient risk stratification including the TNM and BCLC systems. We validated the model in 231 patients from five multicentred cohorts, achieving a real-world accuracy of 82.2% and specificity of 85.7%. The predictive power of these biomarkers emerged through the integration of their spatial distributions, rather than individual marker expression levels alone. In vivo models, including NK cell-specific Spon2-knockout mice, revealed that SPON2 enhances IFNγ secretion and NK cell infiltration at the invasive front. Our study introduces TIMES, a publicly accessible tool for predicting HCC recurrence risk, offering insights into its potential to inform treatment decisions for early-stage HCC.