2025-06-13 国立遺伝学研究所
<関連情報>
- https://www.nig.ac.jp/nig/ja/2025/06/research-highlights_ja/rh20250527.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-03301-3
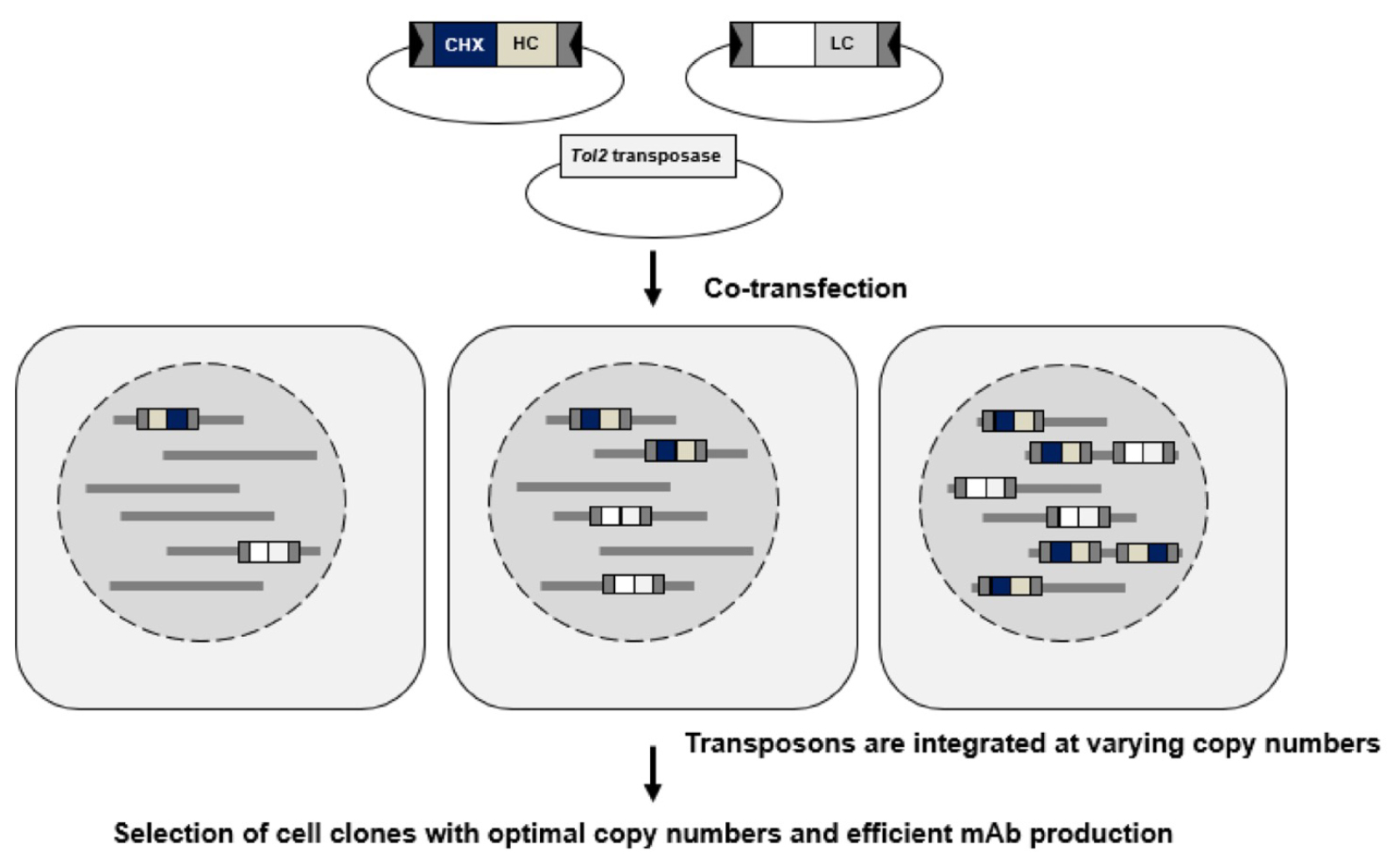
トランスポザーゼを介したサブユニット分割ベクターの統合によるCHO細胞でのマルチサブユニットタンパク質の生産 Production of multi-subunit proteins in CHO cells by transposase-mediated integration of subunit-splitting vectors
Keina Yamaguchi,Risa Ogawa,Masayoshi Tsukahara & Koichi Kawakami
Scientific Reports Published:27 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-03301-3
Abstract
The Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line is a widely employed system for producing therapeutic proteins. In our previous study, we established an efficient method for generating stable cell lines by utilizing the Tol2 transposon system, combined with cycloheximide (CHX) resistance as a selection marker. This DNA-based transposon allows the integration of the gene of interest into various genomic loci within the host cell genome. To further develop this system, we performed gene transfer using single vectors carrying each subunit separately, rather than using dual vector linking subunits in tandem, to express monoclonal antibodies. The resulting cell lines exhibited stable protein production for an extended period of up to 12 weeks, as well as high productivity in fed-batch cultures. We found that the copy numbers of vector construct integrated in the genome varied for different mAbs, suggesting these cell lines maintained the vector constructs at copy numbers for effective gene expression. This study highlights the potential usefulness of the Tol2 transposon system in producing multi-subunit proteins, such as bispecific antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins, thereby promoting advancements in biopharmaceutical production.